Page 200 - IJB-10-1
P. 200
International Journal of Bioprinting Nanoclay biopolymer inks for 3D printing
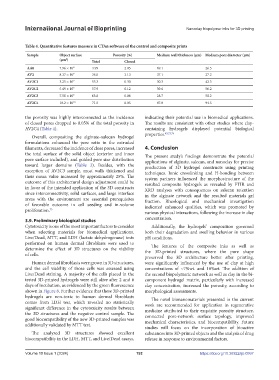
Table 4. Quantitative features measure in CTAn software of the control and composite prints
Sample Object surface Porosity (%) Medium wall thickness (µm) Medium pore diameter (µm)
(µm ) Total Closed
2
AA0 7.96 × 10 8 4.99 2.05 69.1 26.5
AV2 8.37 × 10 9 36.0 3.13 37.1 27.2
AV2C1 3.25 × 10 9 53.3 0.30 30.3 42.3
AV2C2 5.49 × 10 9 57.9 0.12 39.6 56.2
AV2C3 7.58 × 10 9 63.8 0.08 28.7 58.2
AV2C4 10.2 × 10 10 71.5 0.05 47.8 94.5
the porosity was highly interconnected as the incidence indicating their potential use in biomedical applications.
of closed pores dropped to 0.05% of the total porosity in The results are consistent with other studies where clay-
AV2C4 (Table 4). containing hydrogels displayed potential biological
Overall, compositing the alginate–salecan hydrogel properties. 42,73,76
formulations enhanced the pore ratio in the extruded
filaments, decreased the incidence of close pores, increased 4. Conclusion
the total surface of the solid object (exterior and inner The present study’s findings demonstrate the potential
pore surface included), and guided pore size distribution applications of alginate, salecan, and nanoclay for precise
toward larger domains (Table 3). Besides, with the production of 3D hydrogel constructs using printing
exception of AV2C3 sample, most walls thickened and techniques. Ionic crosslinking and H-bonding between
their mean value increased by approximately 25%. The system partners influenced the morphostructure of the
outcome of this architectural design adjustment could be resulted composite hydrogels as revealed by FTIR and
in favor of the intended application of the 3D constructs XRD analyses with consequences on salecan retention
since interconnectivity, solid surfaces, and large interface in the alginate network and the resulted materials gel
areas with the environment are essential prerequisites fraction. Rheological and mechanical investigation
of favorable outcome in cell seeding and in-volume indicated enhanced qualities, which was promoted by
proliferation. 75 various physical interactions, following the increase in clay
3.9. Preliminary biological studies concentration.
Cytotoxicity is one of the most important factors to consider Additionally, the hydrogels’ composition governed
when selecting materials for biomedical applications. both their degradation and swelling behavior in various
Live/Dead, MTT, and LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) tests pH conditions.
performed on human dermal fibroblasts were used to The features of the composite inks as well as
determine the effect of 3D structures on the viability the 3D-printed structures, where the pore shape
of cells.
preserved the 3D architecture better after printing,
Human dermal fibroblasts were grown in 3D structures, were significantly influenced by the use of clay at high
and the cell viability of those cells was assessed using concentrations of ~7%wt. and 10%wt. The addition of
Live/Dead staining. A majority of the cells placed in the the second biopolymeric network as well as clay in the bi-
tested 3D-printed hydrogels were still alive after 2 and 6 component hydrogel matrix, particularly with increased
days of incubation, as evidenced by the green fluorescence clay concentration, increased the porosity, according to
shown in Figure 8. Further evidence that these 3D-printed morphological assessments.
hydrogels are non-toxic to human dermal fibroblasts The novel bionanomaterials presented in the current
comes from LDH test, which revealed no statistically work are recommended for application in regenerative
significant difference in the cytotoxicity results between medicine attributed to their exquisite porosity structure,
the 3D structures and the negative control sample. The connected pore-network surface topology, improved
good biocompatibility of the new 3D-printed samples was mechanical characteristics, and biocompatibility. Future
additionally validated by MTT test.
studies will focus on the incorporation of bioactive
The analyzed 3D structures showed excellent substances into 3D-printed objects and the analysis of drug
biocompatibility in the LDH, MTT, and Live/Dead assays, release in response to environmental factors.
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 192 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0967