Page 254 - IJB-10-1
P. 254
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed hydrogel with antioxidant activity
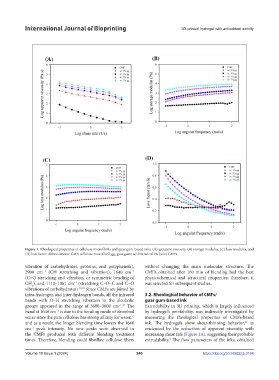
Figure 1. Rheological properties of cellulose microfibrils and guar gum-based inks: (A) apparent viscosity, (B) storage modulus, (C) loss modulus, and
(D) loss factor. Abbreviations: CMF, cellulose microfibril; gg, guar gum; w/,100 mL of 1% (w/v) CMFs.
vibration of carbohydrates, proteins, and polyphenols), without changing the main molecular structure. The
−1
−1
2900 cm (CH stretching and vibration), 1640 cm CMFs obtained after 160 min of blending had the best
(C=O stretching and vibration, or symmetric bending of physicochemical and structural properties; therefore, it
−1
CH ), and 1110–1061 cm (stretching C–O–C and C–O was selected for subsequent studies.
2
vibrations of carbohydrates). 30,31 Since CMFs are joined by
intra-hydrogen and inter-hydrogen bonds, all the infrared 3.2. Rheological behavior of CMFs/
bands with O–H stretching vibration in the alcoholic guar gum-based ink
−1 32
groups appeared in the range of 3600–3000 cm . The Extrudability in 3D printing, which is largely influenced
−1
band at 1640 cm is due to the bending mode of absorbed by hydrogel’s printability, was indirectly investigated by
33
water since the pure cellulose has strong affinity for water, measuring the rheological properties of CMFs-based
24
and as a result, the longer blending time lowers the 1640 ink. The hydrogels show shear-thinning behavior, as
cm peak intensity. No new peaks were observed in evidenced by the reduction of apparent viscosity with
−1
the CMFs produced with different blending treatment increasing shear rate (Figure 1A), suggesting their probable
5
times. Therefore, blending could fibrillate cellulose fibers extrudability. The flow parameters of the inks, obtained
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 246 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0164