Page 152 - IJB-10-2
P. 152
International Journal of Bioprinting dECM bioink for in vitro disease modeling
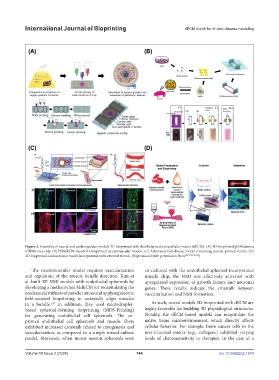
Figure 3. Examples of neural and cardiovascular models 3D-bioprinted with decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM). (A) 3D-bioprinted glioblastoma
(GBM) on a chip. (B) PNSdECM-based 3D-bioprinted neuromuscular models. (C) Atherosclerosis disease model containing coaxial-printed vessels. (D)
3D-bioprinted cardiac tissue model incorporated with external stimuli. (Reproduced with permission from 106,142,146,162 )
The neuromuscular model requires vascularization co-cultured with the endothelial spheroid-incorporated
and regulation of the muscle bundle direction. Kim et muscle chip, the NMJ was effectively activated with
al. built 3D NMJ models with endothelial spheroids by upregulated expression of growth factors and neuronal
developing a methacrylate MdECM for recapitulating the genes. These results indicate the crosstalk between
mechanical stiffness of muscle tissues and applying electric vascularization and NMJ formation.
field-assisted bioprinting to uniaxially align muscles
in a bundle. In addition, they used microdroplet- As such, neural models 3D-bioprinted with dECM are
147
based spheroid-forming bioprinting (MDS-Printing) highly favorable for building 3D physiological structures.
for generating endothelial cell spheroids. The co- Notably, the dECM-based models can recapitulate the
printed endothelial cell spheroids and muscle fibers native tissue microenvironment, which directly affects
exhibited increased crosstalk related to myogenesis and cellular behavior. For example, brain cancer cells in the
vascularization, as compared to a simply mixed culture non-neuronal matrix (e.g., collagens) exhibited varying
model. Moreover, when motor neuron spheroids were levels of chemosensitivity to therapies. In the case of a
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 144 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1970