Page 17 - IJB-10-3
P. 17
International Journal of Bioprinting Supramolecular hydrogels as bioinks
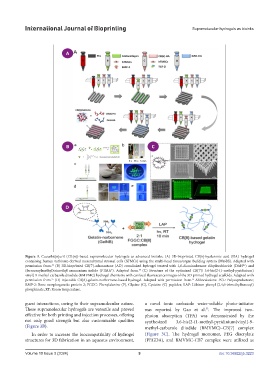
Figure 3. Cucurbit[n]uril (CB[n])-based supramolecular hydrogels as advanced bioinks. (A) 3D-bioprinted CB[6]-hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogel
containing human turbinate-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (hTMCs) using the multi-head tissue/organ building system (MtoBS). Adapted with
53
2+
permission from. (B) 3D-bioprinted CB[7]-adamantane (AD) crosslinked hydrogel treated with 1,6-diaminohexane dihydrochloride (DAH ) and
54
(ferrocenylmethyl)trimethyl ammonium iodide (FTMA ). Adapted from. (C) Structure of the optimized CB[7]/ 3,6-bis[2-(1-methyl-pyridinium)
+
vinyl]-9-methyl-carbazole diiodide (BMVMC) hydrogel chemistry with confocal fluorescence images of the 3D-printed hydrogel scaffolds. Adapted with
56
permission from. (D) Injectable CB[8]-gelatin-norbornene-based hydrogel. Adapted with permission from. Abbreviations: PCL: Polycaprolactone;
55
BMP-2: Bone morphogenetic protein 2; FGGC: Phenylalanine (F), Glycine (G), Cysteine (C) peptides; LAP: Lithium phenyl (2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)
phosphinate; RT: Room temperature.
guest interactions, owing to their supramolecular nature. a novel ionic carbazole water-soluble photo-initiator
These supramolecular hydrogels are versatile and proved was reported by Gao et al. . The improved two-
55
effective for both printing and injection processes, offering photon absorption (TPA) was demonstrated by the
not only good strength but also customizable qualities synthesized 3,6-bis[2-(1-methyl-pyridinium)vinyl]-9-
(Figure 3B). methyl-carbazole diiodide (BMVMC)–CB[7] complex
In order to increase the biocompatibility of hydrogel (Figure 3C). The hydrogel monomer, PEG diacrylate
structures for 3D fabrication in an aqueous environment, (PEGDA), and BMVMC-CB7 complex were utilized as
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 9 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3223