Page 24 - IJB-10-3
P. 24
International Journal of Bioprinting Supramolecular hydrogels as bioinks
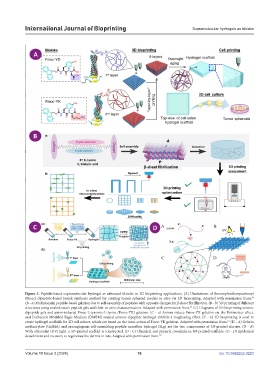
Figure 5. Peptide-based supramolecular hydrogel as advanced bioinks in 3D bioprinting applications. (A) Illustrations of fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl
96
(Fmoc)-dipeptide-based bioink synthesis method for creating tumor spheroid models in vitro via 3D bioprinting. Adapted with permission from.
(B - a) Multidomain peptide-based gelation due to self-assembly of peptides with opposite charges for β-sheet fibrillization. (B - b) 3D printing of different
97
structures using multidomain peptide gels and their in vitro characterization. Adapted with permission from. (C) Diagrams of 3D bioprinting anionic
dipeptide gels and anion-induced Fmoc-L-tyrosine-L-lysine (Fmoc-YK) gelation. (C - a) Anions induce Fmoc-YK gelation via the Hofmeister effect,
and Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM)-soaked anionic dipeptide hydrogel exhibits a toughening effect. (C - b) 3D bioprinting is used to
51
create hydrogel scaffolds for 3D cell culture, which are based on the ionic action of Fmoc-YK gelation. Adapted with permission from. (D - A) Gelatin
methacrylate (GelMA) and proangiogenic self-assembling peptide nanofiber hydrogel (SLg) are the two components of 3D-printed slurries. (D - B)
With ultraviolet (UV) light, a 3D-printed scaffold is constructed. (D - C) Chemical and physical crosslinks in 3D-printed scaffolds. (D - D) Epidermal
detachment and recovery to regenerate the dermis in rats. Adapted with permission from. 98
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 16 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3223