Page 531 - IJB-10-4
P. 531
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printed substrate for adhesion tests
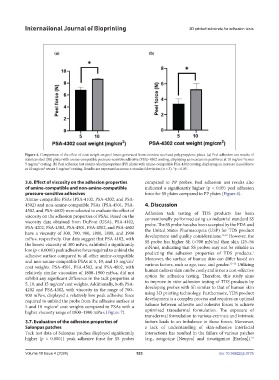
Figure 4. Comparison of the effect of coat weight on peel forces generated from stainless steel and polypropylene plates. (a) Peel adhesion test results of
stainless steel (SS) plates with amine-compatible pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA)-4302 coating, displaying an increase in peel force at 10 mg/cm versus
2
5 mg/cm coating. (b) Peel adhesion test results of polypropylene (PP) plates with amine-compatible PSA-4302 coating, displaying an increase in peel force
2
at 10 mg/cm versus 5 mg/cm coating. Results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). *p < 0.05.
2
2
3.6. Effect of viscosity on the adhesion properties compared to PP probes. Peel adhesion test results also
of amine-compatible and non-amine-compatible indicated a significantly higher (p < 0.05) peel adhesion
pressure-sensitive adhesives force for SS plates compared to PP plates (Figure 8).
Amine-compatible PSAs (PSA-4102, PSA-4202, and PSA-
4302) and non-amine-compatible PSAs (PSA-4501, PSA- 4. Discussion
4502, and PSA-4602) were selected to evaluate the effect of Adhesion tack testing of TDS products has been
viscosity on the adhesion properties of PSAs. Based on the conventionally performed using an industrial standard SS
viscosity data obtained from DuPont (USA), PSA-4102, probe. The SS probe has also been accepted by the FDA and
PSA-4202, PSA-4302, PSA-4501, PSA-4502, and PSA-4602 the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) for TDS product
have a viscosity of 300, 700, 900, 1800, 1800, and 1900 development and quality considerations. 31,32 However, the
mPa·s, respectively. Our data suggest that PSA 4102, with SS probe has higher SE (>700 mN/m) than skin (25–56
the lowest viscosity of 300 mPa·s, exhibited a significantly mN/m), indicating that SS probes may not be reliable in
low (p < 0.0001) peak adhesive force required to unbind the predicting the adhesion properties of TDS products.
1
adhesive surface compared to all other amine-compatible Moreover, the surface of human skin can differ based on
and non-amine-compatible PSAs at 5, 10, and 15 mg/cm various factors, such as age, race, and gender. 33–36 Utilizing
2
coat weights. PSA-4501, PSA-4502, and PSA-4602, with
relatively similar viscosities of 1800–1900 mPa·s, did not human cadaver skin can be costly and is not a cost-effective
exhibit any significant difference in the tack properties at option for adhesion testing. Therefore, this study aims
5, 10, and 15 mg/cm coat weights. Additionally, both PSA- to improve in vitro adhesion testing of TDS products by
2
4202 and PSA-4302, with viscosity in the range of 700– developing probes with SE similar to that of human skin
900 mPa·s, displayed a relatively low peak adhesive force using 3D printing technology. Furthermore, TDS product
required to unbind the probe from the adhesive surface at development is a complex process and requires an optimal
5 and 10 mg/cm coat weights compared to PSAs with a balance between adhesive and cohesive forces to achieve
2
higher viscosity range of 1800–1900 mPa·s (Figure 7). optimized transdermal formulation. The exposure of
transdermal formulation to various extrinsic and intrinsic
3.7. Evaluation of the adhesion properties of factors leads to an imbalance in these forces. Moreover,
Salonpas patches a lack of understanding of skin-adhesive interfacial
Tack test data of Salonpas patches displayed significantly interactions has resulted in the failure of various patches
higher (p < 0.0001) peak adhesive force for SS probes (e.g., rotigotine [Neupro] and rivastigmine [Exelon]).
10
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 523 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3735