Page 124 - IJB-7-1
P. 124
3D Printed PLA/HAp Biocomposites
A B C
D E F
G H I
J K L
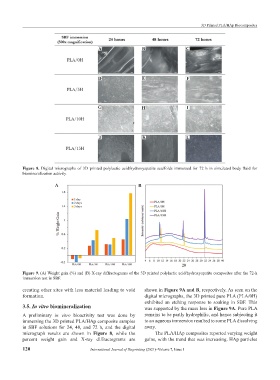
Figure 8. Digital micrographs of 3D printed polylactic acid/hydroxyapatite scaffolds immersed for 72 h in simulated body fluid for
biomineralization activity.
A B
Figure 9. (A) Weight gain (%) and (B) X-ray diffractograms of the 3D printed polylactic acid/hydroxyapatite composites after the 72-h
immersion test in SBF.
creating other sites with less material leading to void shown in Figure 9A and B, respectively. As seen on the
formation. digital micrographs, the 3D printed pure PLA (PLA/0H)
exhibited an etching response to soaking in SBF. This
3.5. In vitro biomineralization was supported by the mass loss in Figure 9A. Pure PLA
A preliminary in vitro bioactivity test was done by remains to be partly hydrophilic, and hence subjecting it
immersing the 3D printed PLA/HAp composite samples to an aqueous immersion resulted to some PLA dissolving
in SBF solutions for 24, 48, and 72 h, and the digital away.
micrograph results are shown in Figure 8, while the The PLA/HAp composites reported varying weight
percent weight gain and X-ray diffractograms are gains, with the trend that was increasing. HAp particles
120 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 1