Page 11 - IJB-8-4
P. 11
Shi, et al.
(Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) solution solution was stirred at room temperature for 1 h using
to reach the final concentration of 15.0 - 16.0 wt% and magnetic stirring, then centrifuged at 3500 rpm/min for
stored at 4°C refrigerator for further use. 10 min, and the final mixture solutions were stored in a
0.3 g SA was dissolved in 9.7 g deionized water at refrigerator at 4°C.
45°C for 30 min to obtain the 3.0 wt% SA solution. To
prepare mixture solutions, the SF solution and the SA 2.3. Extrusion printing of SF scaffolds
solution were mixed in different mass ratios of 1.5:1,
1.8:1, and 2.0:1, which were named Ink 1, Ink 2, and Ink Fisnar liquid dispenser (F4200N.2) with a −20°C RT
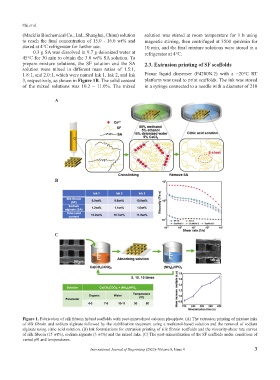
3, respectively, as shown in Figure 1B. The solid content platform was used to print scaffolds. The ink was stored
of the mixed solutions was 10.2 – 11.0%. The mixed in a syringe connected to a needle with a diameter of 210
A
B
C
Figure 1. Fabrication of silk fibroin hybrid scaffolds with post-mineralized calcium phosphate. (A) The extrusion printing of mixture inks
of silk fibroin and sodium alginate followed by the stabilization treatment using a methanol-based solution and the removal of sodium
alginate using citric acid solution. (B) Ink formulations for extrusion printing of silk fibroin scaffolds and the viscosity-shear rate curves
of silk fibroin (15 wt%), sodium alginate (3 wt%) and the mixed inks. (C) The post-mineralization of the SF scaffolds under conditions of
varied pH and temperatures.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4 3