Page 155 - IJB-9-1
P. 155
International Journal of Bioprinting Bio-inks for 3D printing cell microenvironment
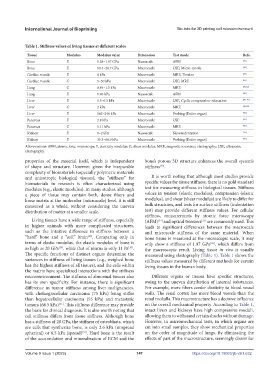
Table 1. Stiffness values of living tissues at different scales
Tissue Modulus Modulus value Dimension Test mode Refs.
Bone E 1.28–1.97 GPa Nanoscale AFM [36]
Bone E 10.4–20.7 GPa Macroscale USE, Micro-tensile [29]
Cardiac muscle E 8 kPa Macroscale MRE, Tension [84]
Cardiac muscle G 5–50 kPa Macroscale USE, MRE [85]
Lung G 0.84–1.5 kPa Macroscale MRE [86,87]
Lung E 1.96 kPa Nanoscale AFM [88]
Liver E 1.5–6.5 kPa Macroscale USE, Cyclic compression-relaxation [89–91]
Liver G 2 kPa Macroscale MRE [92,93]
Liver E 162–248 kPa Macroscale Probing (Entire organ) [94]
Pancreas E 2.8 kPa Macroscale USE [95]
Pancreas G 1.11 kPa Macroscale MRE [96]
Kidney E 1–2 kPa Nanoscale Nanoindentation [74]
Kidney E 35.3–68.9 kPa Macroscale Probing (Entire organ) [94]
Abbreviations: AFM, atomic force microscopy; E, elasticity modulus; G, shear modulus; MRE, magnetic resonance elastography; USE, ultrasonic
elastography.
properties of the material itself, which is independent bone’s porous 3D structure enhances the overall system’s
of shape and structure. However, given the inseparable stiffness .
[33]
complexity of biomaterials (especially polymeric materials
and anisotropic biological tissues), the “stiffness” for It is worth noting that although most studies provide
biomaterials in research is often characterized using specific values for tissue stiffness, there is no gold standard
modulus (e.g., elastic modulus). In many studies, although test for measuring stiffness in biological tissues. Stiffness
a piece of tissue may contain both, dense fibers and values in tension (elastic modulus), compression (elastic
loose matrix at the molecular (microscale) level, it is still modulus), and shear (shear modulus) are likely to differ for
measured as a whole, without considering the uneven bulk structures, and tests for surface stiffness (indentation
distribution of matter at a smaller scale. test) may provide different stiffness values. For cellular
stiffness, measurements by atomic force microscopy
Living tissues have a wide range of stiffness, especially (AFM) and optical tweezers are commonly used. This
[34]
[35]
in higher animals with more complicated structures, leads to significant differences between the macroscale
such as the intuitive difference in stiffness between a and microscale stiffness of the same material. When
“hard” bone and a “soft” brain . Comparing only in bone tissue is measured at the microscopic scale, it may
[28]
terms of elastic modulus, the elastic modulus of bone is only show a stiffness of 1.97 GPa , which differs from
[36]
as high as 20 GPa , while that of mucus is only 11 Pa . the macroscopic result. Living tissue in vivo is usually
[29]
[30]
The specific functions of distinct organs determine the measured using elastography (Table 1). Table 1 shows the
variances in stiffness of living tissues (e.g., weighed bone stiffness values measured by different methods for certain
has the highest stiffness of all tissues), and the cells within living tissues in the human body.
the matrix have specialized interactions with the stiffness
microenvironment. The stiffness of abnormal tissues also Different organs or tissues have specific structures,
has its own specificity. For instance, there is significant owing to the uneven distribution of internal substances.
difference in tumor stiffness among liver malignancies, For example, more fibers confer elasticity to blood vessel
with cholangiocellular carcinoma (75 kPa) being stiffer walls. The renal cortex has more blood vessels than the
than hepatocellular carcinoma (55 kPa) and metastatic renal medulla. This macrostructure has a decisive influence
tumors (66.5 kPa) . This stiffness difference may provide on the overall mechanical property. According to Table 1,
[31]
the basis for clinical diagnosis. It is also worth noting that intact livers and kidneys have high compressive moduli,
cell stiffness differs from tissue stiffness. Although bone allowing them to withstand certain shocks without damage.
has a stiffness of 20 GPa, the stiffness of osteoblasts, which However, in micromechanical tests, in which organs are
are cells that synthesize bone, is only 2.6 kPa (unspread cut into small samples, they show mechanical properties
spherical) or 6.5 kPa (spread) . Hard bone is the result on the order of magnitude of lungs. By eliminating the
[32]
of the accumulation and mineralization of ECM and the effects of part of the macrostructure, seemingly dissimilar
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 147 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.632