Page 315 - IJB-9-3
P. 315
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinted stem cell niche regenerates muscles
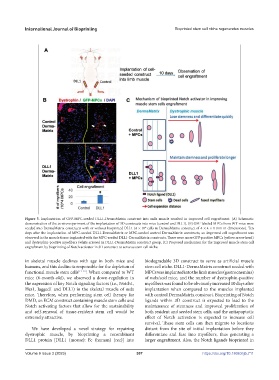
Figure 5. Implantation of GFP-MPC-seeded DLL1-DermaMatrix construct into mdx muscle resulted in improved cell engraftment. (A) Schematic
demonstration of the in vivo experiment of the implantation of 3D constructs into mice (control and DLL1). (B) GFP-labeled MPCs from WT mice were
seeded into DermaMatrix constructs with or without bioprinted DLL1 (4 × 10 cells in DermaMatrix construct of 4 × 4 × 1 mm in dimensions). Ten
4
days after the implantation of MPC-seeded DLL1-DermaMatrix or MPC-seeded control DermaMatrix constructs, an improved cell engraftment was
observed in the muscle tissue implanted with the MPC-seeded DLL1-DermaMatrix constructs. There were more GFP-positive MPCs (yellow arrow head)
and dystrophin-positive myofibers (white arrows) in DLL1-DermaMatrix construct group. (C) Proposed mechanism for the improved muscle stem cell
engraftment by bioprinting of Notch activator in 3D construct to serve as stem cell niche.
in skeletal muscle declines with age in both mice and biodegradable 3D construct to serve as artificial muscle
humans, and this decline is responsible for the depletion of stem cell niche. DLL1-DermaMatrix construct seeded with
functional muscle stem cells [11-13] . When compared to WT MPCs was implanted into the limb muscles (gastrocnemius)
mice (6-month-old), we observed a down-regulation in of mdx/scid mice, and the number of dystrophin-positive
the expression of key Notch signaling factors (i.e., Notch1, myofibers was found to be obviously increased 10 days after
Hes1, Jagged1 and DLL1) in the skeletal muscle of mdx implantation when compared to the muscles implanted
mice. Therefore, when performing stem cell therapy for with control DermaMatrix construct. Bioprinting of Notch
DMD, an ECM construct containing muscle stem cells and ligands within 3D construct is expected to lead to the
Notch activating factors that allow for the sustainability maintenance of stemness and improved proliferation of
and self-renewal of tissue-resident stem cell would be both resident and seeded stem cells, and the antiapoptotic
extremely attractive. effect of Notch activation is expected to increase cell
survival. These stem cells can then migrate to locations
We have developed a novel strategy for repairing distant from the site of initial implantation before they
dystrophic muscle, by bioprinting a recombinant differentiate and fuse into myofibers, thus generating a
DLL1 protein [DLL1 (mouse): Fc (human) (rec)] into larger engraftment. Also, the Notch ligands bioprinted in
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 307 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.711