Page 16 - IJB-9-5
P. 16
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printed edible bird’s nests
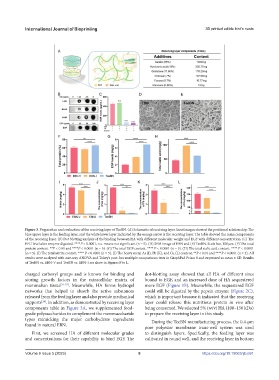
Figure 3. Preparation and evaluation of the receiving layer of TeeBN. (A) Schematic of receiving layer. Inset images showed the positional relationship: The
blue upper layer is the feeding layer, and the white lower layer indicated by the orange arrow is the receiving layer. The table showed the main components
of the receiving layer. (B) Dot blotting analysis of the binding between HA with different molecular weight and EGF with different concentration. (C) The
EFG level after enzyme digested. ****P < 0.0001, n.s. means not significant (n = 5). (D) SEM image of EBN and (E) TeeBN. Scale bar, 100 μm. (F) The total
protein content. **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001 (n = 5). (G) The total EGF content. **** P < 0.0001 (n = 5). (H) The total sialic acid content. **** P < 0.0001
(n = 5). (I) The total nitrite content. **** P < 0.0001 (n = 5). (J) The heavy metal As (J), Pb (K), and Cu (L) content. **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001 (n = 3). All
results were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc multiple comparisons tests in GraphPad Prism 8 and expressed as mean ± SD. Results
of TeeBN vs. EBN-V and TeeBN vs. EBN-I are show in Figures F to L.
charged carboxyl groups and is known for binding and dot-blotting assay showed that all HA of different sizes
storing growth factors in the extracellular matrix of bound to EGF, and an increased dose of HA sequestered
mammalian tissue [31-33] . Meanwhile, HA forms hydrogel more EGF (Figure 3B). Meanwhile, the sequestered EGF
networks that helped to absorb the active substances could still be digested by the pepsin enzyme (Figure 2C),
released from the feeding layer and also provide mechanical which is important because it indicated that the receiving
supports . In addition, as demonstrated by receiving layer layer could release this nutritious protein in vivo after
[34]
components table in Figure 3A, we supplemented food- being consumed. We selected 5% (w/v) HA (100–150 kDa)
grade polysaccharides to complement the monosaccharide to prepare the receiving layer in this study.
types mimicking the major carbohydrate ingredients During the TeeBN manufacturing process, the 0.4-μm
found in natural EBN. pore polyester membrane trans-well system was used
First, we screened HA of different molecular grades to distinguish layers. Specifically, the feeding layer was
and concentrations for their capability to bind EGF. The cultivated in round well, and the receiving layer in bottom
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 8 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.691