Page 146 - v11i4
P. 146
International Journal of Bioprinting AI for sustainable bioprinting
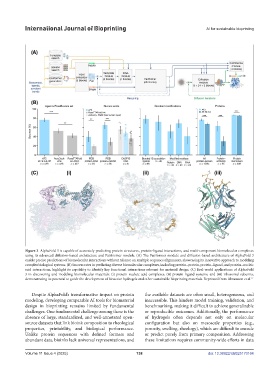
Figure 3. AlphaFold 3 is capable of accurately predicting protein structures, protein–ligand interactions, and multi-component biomolecular complexes
using its advanced diffusion-based architecture and Pairformer module. (A) The Pairformer module and diffusion-based architecture of AlphaFold 3
enable precise predictions of biomolecular interactions without reliance on multiple sequence alignments, showcasing its innovative approach to modeling
complex biological systems. (B) Success rates in predicting diverse biomolecular complexes, including protein–protein, protein–ligand, and protein–nucleic
acid interactions, highlight its capability to identify key functional interactions relevant for material design. (C) Real-world applications of AlphaFold
3 in discovering and modeling biomolecular materials: (i) protein–nucleic acid complexes, (ii) protein–ligand systems, and (iii) ribosomal subunits,
demonstrating its potential to guide the development of bioactive hydrogels and other sustainable bioprinting materials. Reprinted from Abramson et al.
17
Despite AlphaFold’s transformative impact on protein the available datasets are often small, heterogeneous, and
modeling, developing comparable AI tools for biomaterial inaccessible. This hinders model training, validation, and
design in bioprinting remains limited by fundamental benchmarking, making it difficult to achieve generalizable
challenges. One fundamental challenge among these is the or reproducible outcomes. Additionally, the performance
absence of large, standardized, and well-annotated open- of hydrogels often depends not only on molecular
source datasets that link bioink composition to rheological configuration but also on mesoscale properties (e.g.,
properties, printability, and biological performance. porosity, swelling, rheology), which are difficult to encode
Unlike protein sequences with defined formats and or predict purely from primary composition. Addressing
abundant data, bioinks lack universal representations, and these limitations requires community-wide efforts in data
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 138 doi: 10.36922/IJB025170164