Page 43 - IJPS-10-3
P. 43
International Journal of
Population Studies Traditional practices of herbal medicine in Malawi
Perceived benefits vs.
Perceived barriers
Modifying
variables
Perceived threat
Likelihood of engaging
Perceived in health promoting
seriousness behavior
Self-efficacy
Perceived
susceptibility
Cues to action
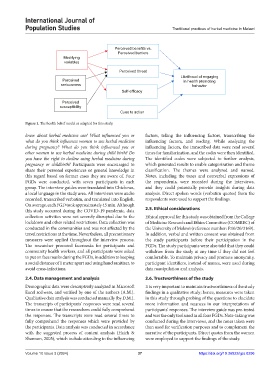
Figure 1. The health belief model as adapted for this study.
know about herbal medicine use? What influenced you or factors, telling the influencing factors, transcribing the
what do you think influences women to use herbal medicine influencing factors, and reading. While analyzing the
during pregnancy? What do you think influenced you or influencing factors, the transcribed data were read several
other women to use herbal medicine during child birth? Do times for familiarization, and the codes were then identified.
you have the right to decline using herbal medicine during The identified codes were subjected to further analysis,
pregnancy or childbirth? Participants were encouraged to which generated results to enable categorization and theme
share their personal experiences or general knowledge in classification. The themes were analyzed and named.
this regard based on former cases they are aware of. Four Notes, including the tones and nonverbal expressions of
FGDs were conducted, with seven participants in each the respondents, were recorded during the interviews,
group. The interview guides were translated into Chichewa, and they could potentially provide insights during data
a local language in the study area. All interviews were audio analysis. Direct spoken words (verbatim quotes) from the
recorded, transcribed verbatim, and translated into English. respondents were used to support the findings.
On average, each FGD took approximately 45 min. Although
this study occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic, data 2.5. Ethical considerations
collection activities were not severely disrupted due to the Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the College
lockdown and other related restrictions. Data collection was of Medicine Research and Ethics Committee (COMREC) of
conducted in the communities and was not affected by the the University of Malawi (reference number: P.10/20/3169).
travel restrictions at the time. Nevertheless, all precautionary In addition, verbal and written consent was obtained from
measures were applied throughout the interview process. the study participants before their participation in the
The researcher procured facemasks for participants and FGDs. The study participants were also told that they could
community health workers, and all participants were asked withdraw from the study at any time if they did not feel
to put on face masks during the FGDs, in addition to keeping comfortable. To maintain privacy and promote anonymity,
a social distance of 1 meter apart and using hand sanitizer, to participant identifiers, instead of names, were used during
avoid cross-infections. data manipulation and analysis.
2.4. Data management and analysis 2.6. Trustworthiness of the study
Demographic data were descriptively analyzed in Microsoft It is very important to maintain trustworthiness of the study
Excel software, and verified by one of the authors (A.M.). findings in a qualitative study; hence, measures were taken
Qualitative data analysis was conducted manually (by D.M.). in this study through probing of the questions to elucidate
The transcripts of participants’ responses were read several more information and nuances in our interpretations of
times to ensure that the researchers could fully comprehend participants’ responses. The interview guide was pre-tested
the responses. The transcripts were read several times to and was the only tool used in all four FGDs. Note-taking was
fully comprehend the responses which were provided by conducted during the interviews, and the notes taken were
the participants. Data analysis was conducted in accordance then used for verification purposes and to complement the
with the suggested process of content analysis (Hsieh & narrative of the participants. Direct quotes from the women
Shannon, 2005), which include attending to the influencing were employed to support the findings of the study.
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 37 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.0296