Page 30 - IJPS-10-4
P. 30
International Journal of
Population Studies Chemsex among MSM during the COVID-19 pandemic
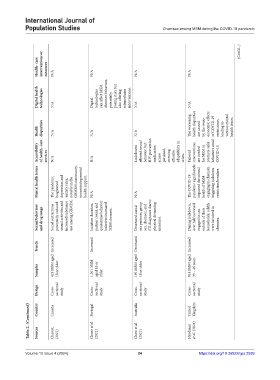
Health‑ care interventions or measures N/A N/A N/A N/A (Cont’d...)
Digital health technologies N/A Digital technologies can affect MSM chemsex behaviors, potentially posing risks but also offering telemedicine interventions. N/A N/A
Health disparities N/A N/A N/A The worsening health disparities are caused by the socio- economic effects of COVID-19 restrictions, leading to various mental health issues.
Accessibility of health‑ care services N/A N/A Lockdowns affected sexual behavior, but HIV prevention medication access persisted, stressing effective adaptability in crises. Tailored interventions are needed for MSM to promote safer behaviors amid COVID-19.
Mental health issues The pandemic heightened depression and anxiety rates, notably in the GBMSM community, necessitating mental health support. N/A N/A The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted the mental health of MSM engaging in chemsex, triggering lockdown restriction breaches.
Sexual behaviors and drug usage Social restrictions potentially reduced sexual activities and increased substance use among GBMSM. Isolation duration, partner count, and quarantine behavior linked to increased MSM chemsex. Decreased casual sex partners, group sex, chemsex, and STI diagnoses due to physical distancing measures. During lockdown, over half surveyed engaged in sex outside of their households; a fifth
Trends Increased Increased Decreased Increased
Samples 423 MSM aged 18 or older 1,301 MSM aged 18 or older 192 MSM aged 18 or older 814 MSM aged 33 – 46 years
Design Cross- sectional study Cross- sectional study Cross- sectional study Cross- sectional study
Table 2. (Continued) Country Sources Canada Charest, (2021) Portugal Chone et al. (2021) Australia Chow et al. (2021) United Hyndman Kingdom et al. (2021)
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 24 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.2599