Page 119 - IJPS-11-1
P. 119
International Journal of
Population Studies Developing individual active aging measurement tool
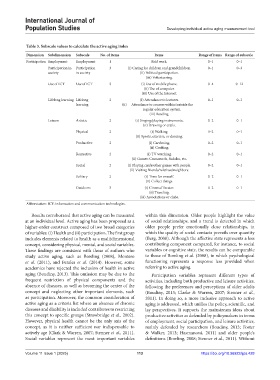
Table 3. Subscale values to calculate the active aging index
Dimension Subdimension Subscale No. of items Items Range of items Range of subscale
Participation Employment Employment 1 Paid work. 0–1 0–1
Participation in Participation 3 (i) Caring for children and grandchildren. 0–1 0–3
society in society (ii) Political participation.
(iii) Volunteering.
Use of ICT Use of ICT 3 (i) Use of mobile phone. 0–4 0–12
(ii) Use of computer.
(iii) Use of the Internet.
Lifelong learning Lifelong 2 (i) Attendance to lectures. 0–1 0–1
learning (ii) Attendance to courses within/outside the
regular education system.
(iii) Reading.
Leisure Artistic 2 (i) Singing/playing instruments. 0–2 0–1
(ii) Drawing or crafts.
Physical 2 (i) Walking. 0–2 0–1
(ii) Sports, exercise, or dancing.
Productive 2 (i) Gardening. 0–2 0–1
(ii) Cooking.
Recreative 2 (i) TV watching. 0–2 0–1
(ii) Games: Crosswords, Sudoku, etc.
Social 2 (i) Playing cards/other games with people. 0–2 0–1
(ii) Visiting friends/relatives/neighbors.
Solitary 2 (i) Time for oneself. 0–2 0–1
(ii) Collect things.
Outdoors 3 (i) Cinema/Theater. 0–2 0–1
(ii) Traveling.
(iii) Associations or clubs.
Abbreviation: ICT: Information and communication technologies.
Results corroborated that active aging can be measured within this dimension. Older people highlight the value
at an individual level. Active aging has been proposed as a of social relationships, and a trend is detected in which
higher-order construct composed of two broad categories older people prefer emotionally close relationships, in
of variables: (i) Health and (ii) participation. The first group which the quality of social contacts prevails over quantity
includes elements related to health as a multidimensional (Berg, 2008). Although the affective state represents a less
concept, considering physical, mental, and social variables. contributing component compared, for instance, to social
These findings are consistent with those of authors who variables or cognitive state, the results can be comparable
study active aging, such as Bowling (2008), Montero to those of Bowling et al. (2008), in which psychological
et al. (2011), and Perales et al. (2014). However, some functioning represents a response less provided when
academics have rejected the inclusion of health in active referring to active aging.
aging (Boudiny, 2013). This omission may be due to the Participation variables represent different types of
frequent restriction of physical components and the activities, including both productive and leisure activities,
absence of diseases, as well as becoming the center of the following the preferences and perceptions of older adults
concept and neglecting other important elements, such (Boudiny, 2013; Clarke & Warren, 2007; Stenner et al.,
as participation. Moreover, the common consideration of 2011). In doing so, a more inclusive approach to active
active aging as a criteria list where an absence of chronic aging is addressed, which unifies the policy, scientific, and
diseases and disability is included contributes to restricting lay perspectives. It supports the mainstream ideas about
this concept to specific groups (Strawbridge et al., 2002). productive activities as defended by policymakers in terms
However, physical health cannot be the only axis of the of employment, social participation, and leisure activities,
concept, as it is neither sufficient nor indispensable to mainly defended by researchers (Boudiny, 2013; Foster
actively age (Clark & Warren, 2007; Stenner et al., 2011). & Walker, 2013; Hasmanová, 2011) and older people’s
Social variables represent the most important variables definitions (Bowling, 2008; Stenner et al., 2011). Without
Volume 11 Issue 1 (2025) 113 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.428