Page 48 - IJPS-11-1
P. 48
International Journal of
Population Studies Age, gender, internet and older adults’ cognition
Table 2. Multilinear regression coefficients on predicting sample’s cognition
Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Model 4 Model 5
β SE β SE β SE β SE β SE
Race −1.922*** 0.150 −1.939*** 0.150 −1.936*** 0.150 −1.936*** 0.150 −1.931*** 0.150
Married or partnered 0.089 0.127 0.078 0.127 0.260* 0.132 0.283* 0.132 0.279* 0.132
Years of education 0.388*** 0.023 0.390*** 0.023 0.393*** 0.023 0.396*** 0.023 0.397*** 0.023
Light activities 0.201** 0.063 0.198** 0.063 0.127* 0.064 0.125 0.064 0.118 0.064
Moderate activities 0.062 0.054 0.060 0.054 0.080 0.054 0.080 0.054 0.081 0.054
Vigorous activities −0.131* 0.052 −0.131* 0.052 −0.094 0.052 −0.095 0.052 −0.093 0.052
Smoke status −0.541** 0.205 −0.556** 0.205 −0.522* 0.204 −0.532** 0.204 −0.508* 0.204
Drink per week 0.008 0.010 0.007 0.010 0.016 0.010 0.013 0.010 0.014 0.010
High blood pressure −0.016 0.134 −0.025 0.134 −0.013 0.134 −0.012 0.134 −0.019 0.134
Diabetes −0.152 0.143 −0.161 0.143 −0.105 0.143 −0.085 0.143 −0.092 0.143
Cancer 0.241 0.157 0.233 0.157 0.252 0.157 0.260 0.157 0.258 0.157
Depression −0.071 0.037 −0.073* 0.037 −0.086* 0.037 −0.083* 0.037 −0.081* 0.037
ADL −0.038 0.093 −0.036 0.093 −0.047 0.093 −0.052 0.093 −0.051 0.093
IADL −0.763*** 0.112 −0.753*** 0.112 −0.754*** 0.112 −0.760*** 0.112 −0.760*** 0.112
Self-rated health 0.220** 0.072 0.226** 0.072 0.222** 0.072 0.212** 0.072 0.213** 0.072
(dev) Internet use 0.370*** 0.027 0.346*** 0.030 0.336*** 0.030 0.286*** 0.041 0.316*** 0.043
(dev) Age −0.091*** 0.007 −0.091*** 0.007 −0.092*** 0.007 −0.111*** 0.009 −0.110*** 0.009
(dev) Internet use×(dev) age 0.004+ 0.002 0.004 0.002 0.004 0.002 −0.002 0.003
Gender (ref: men) 0.685*** 0.134 0.597*** 0.139 0.689** 0.145
(dev) Internet use×gender 0.091+ 0.048 0.034 0.055
(dev) Age×gender 0.033** 0.012 0.033** 0.012
(dev) Internet use×(dev) age×gender 0.010* 0.005
R 2 0.356 0.357 0.361 0.362 0.363
F 125.90 119.12 114.95 104.62 100.16
Notes: “dev” stands for mean deviation; “e” stands for exponent; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
Abbreviations: ADL: Activities of daily living; IADL: Instrumental activities of daily living.
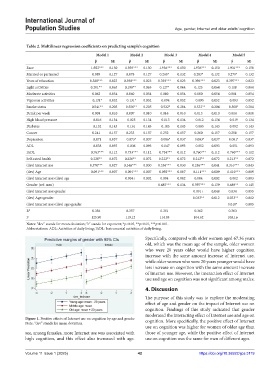
Specifically, compared with older women aged 67.36 years
old, which was the mean age of the sample, older women
who were 20 years older would have higher cognition
increase with the same amount increase of Internet use,
while older women who were 20 years younger would have
less increase on cognition with the same amount increase
of Internet use. However, the interaction effect of Internet
use and age on cognition was not significant among males.
4. Discussion
The purpose of this study was to explore the moderating
effect of age and gender on the impact of Internet use on
cognition. Findings of this study indicated that gender
moderated the interacting effect of Internet use and age on
Figure 1. Positive effects of Internet use on cognition by age and gender cognition. More specifically, the positive effect of Internet
Note: “dev” stands for mean deviation.
use on cognition was higher for women of older age than
see, among females, more Internet use was associated with those of younger age, while the positive effect of Internet
high cognition, and this effect also increased with age. use on cognition was the same for men of different ages.
Volume 11 Issue 1 (2025) 42 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.3119