Page 101 - IJPS-11-4
P. 101
International Journal of
Population Studies Health disparities and older adults well-being in China
compared to living in rural areas. Moreover, the estimated In this study, we aimed to analyze the health status
coefficients of explanatory variables reveal differences in of older adults from three different perspectives.
cognitive abilities even among the older adults residing in Irrespective of the specific health status being evaluated,
cities, depending on their household registration status. we incorporated two dummy variables into each regression
In essence, household registration reflects the cumulative model: (i) whether the household has savings and (ii)
effects of socioeconomic status throughout the life cycle, whether the household is located in the Yangtze River
contributing to health disparities. Delta or the Pearl River Delta region. Our empirical results
Regarding Communist Party of China membership, indicate that having savings has a statistically significant
older-aged party members demonstrate superior cognitive positive effect on the health condition of the Chinese
abilities compared to non-party members. In China, both older adults, regardless of their health status. In addition,
the health-care system and social welfare system prioritize the dummy variable for developed regions demonstrates
the members of the Communist Party of China, signifying
an aristocratic status among party members in Chinese Table 5. Estimated results concerning physical, mental, and
society, particularly the old-age. In addition, most of those cognitive health (ADLs≥1, IADLs≥1, CESD≥10, MMSE≤23)
who manage to become party members originate from the Variables Model 7
elite class in society. To investigate the impact of physical Coefficient SE
and mental health on cognitive health, we extended model
5 by incorporating two new explanatory variables to form Age 0.080 0.006***
model 6: IADLs and CESD. These variables represent Age square −0.001 0.000***
physical health and mental health, respectively. The results Gender 0.011 0.008
obtained from model 6 indicate that both health variables Married 0.033 0.028
have statistically significant and positive effects on the One-person household −0.003 0.028
cognitive ability of the older adults. Notably, physical health Education level
has a particularly significant effect on cognitive ability.
Illiterate (reference)
Finally, our analysis of physical, mental, and cognitive Did not finish primary school 0.038 0.010***
health (Table 5) revealed that the explanatory variable Elementary school 0.109 0.011***
“age” and its quadratic term both have statistically
significant effects. In addition, most of the socioeconomic Middle school 0.161 0.012***
variables, including education level, household location, High school 0.214 0.015***
and Communist Party of China membership, also exert College degree and above 0.299 0.035***
a statistically significant effect on physical, mental, Household location
and cognitive health. Next, we made a prediction of Rural residence with urban household
the dependent variable while keeping other conditions registration (reference)
constant in Model 7. As people age, the predicted health Urban residence with rural 0.019 0.019
ratio initially increases (predicted dependent variable). household registration (1,1)
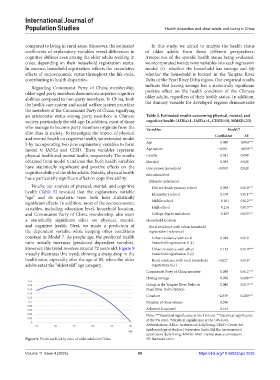
However, this trend reverses around 72 years old. Figure 9 Urban residence with urban 0.112 0.018***
visually illustrates this trend, showing a sharp drop in the household registration (1,0)
health ratio, especially after the age of 85, when the older Rural residence with rural household −0.027 0.016*
adults enter the “oldest old” age category. registration (0,1)
Communist Party of China member 0.056 0.012***
Having savings 0.078 0.008***
Living in the Yangtze River Delta or 0.040 0.013***
Pearl River Delta districts
Constant −2.839 0.200***
Number of observations 8,396
Adjusted R squared 0.161
Note: ***Statistical significance at the 1% level. **Statistical significance
at the 5% level. *Statistical significance at the 10% level.
Abbreviations: ADLs: Activities of daily living; CESD: Center for
Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale; IADLs: Instrumental
activities of daily living; MMSE: Mini-mental state examination;
Figure 9. Predicted healthy ratio of older adults in China SE: Standard error.
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 95 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.2035