Page 98 - IJPS-11-4
P. 98
International Journal of
Population Studies Health disparities and older adults well-being in China
models 1 and 2. In both models, we controlled for personal model 2. While ADLs and IADLs are both indicators of
variables such as age, gender, marital status, and household physical health, ADLs encompass only fundamental daily
type while examining if socioeconomic status affects the activities, whereas IADLs assess the executive functioning
physical health of the older ages. The empirical results involved in more complex daily tasks. Therefore, compared
demonstrate that the one-person household variable has a to the results of ADLs in model 1, IADLs (model 2)
statistically significant positive effect on the physical health are more closely related to socioeconomic status. The
of the older adults. In addition, the coefficients for “gender” coefficients for all education level categories are positive
and “married” are both positive in models 1 and 2. Model and have statistically significant effects on the physical
1 indicates that the probability of physical health in the health of the older people compared to those who are
married group is higher than that in the unmarried group, illiterate. In addition, the interaction variable of household
with the difference being significant at the 5% level. Model location demonstrates that the older people who have
2 demonstrates that the probability of physical health for urban household registration and reside in cities have a
males is higher than for females, with the difference being higher probability of physical health than the reference
significant at the 1% level. group, who have urban household registration but reside
However, we did not find any statistically significant in rural areas.
relationship between socioeconomic status and the ADLs Second, when analyzing mental health (Table 3), unlike
indicator in model 1, even though socioeconomic status previous studies, we found that there is no statistically
variables such as education level and household location significant correlation between the CESD score and age.
have statistically significant positive effects on IADLs in This observation suggests that age may not be an important
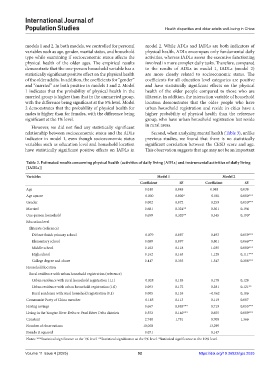
Table 2. Estimated results concerning physical health (activities of daily living [ADLs] and instrumental activities of daily living
[IADLs])
Variables Model 1 Model 2
Coefficient SE Coefficient SE
Age 0.018 0.048 0.048 0.038
Age square −0.000 0.000* −0.001 0.000***
Gender 0.002 0.072 0.259 0.050***
Married 0.681 0.324** 0.301 0.194
One-person household 0.659 0.320** 0.345 0.190*
Education level
Illiterate (reference)
Did not finish primary school −0.079 0.087 0.493 0.059***
Elementary school 0.089 0.097 0.801 0.066***
Middle school 0.102 0.118 1.035 0.080***
High school 0.162 0.163 1.128 0.111***
College degree and above 0.417 0.355 1.547 0.288***
Household location
Rural residence with urban household registration (reference)
Urban residence with rural household registration (1,1) −0.028 0.185 0.178 0.128
Urban residence with urban household registration (1,0) 0.093 0.172 0.281 0.121**
Rural residence with rural household registration (0,1) 0.005 0.155 −0.062 0.106
Communist Party of China member −0.185 0.113 0.119 0.087
Having savings 0.667 0.085*** 0.719 0.055***
Living in the Yangtze River Delta or Pearl River Delta districts 0.552 0.140*** 0.655 0.089***
Constant 2.748 1.781 0.708 1.366
Number of observations 10,050 13,295
Pseudo R squared 0.071 0.147
Notes: ***Statistical significance at the 1% level. **Statistical significance at the 5% level. *Statistical significance at the 10% level.
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 92 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.2035