Page 92 - IJPS-11-4
P. 92
International Journal of
Population Studies Health disparities and older adults well-being in China
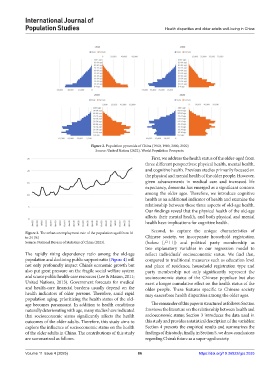
Figure 2. Population pyramids of China (1960, 1980, 2000, 2020)
Source: United Nation (2022), World Population Prospects.
First, we address the health status of the older-aged from
three different perspectives: physical health, mental health,
and cognitive health. Previous studies primarily focused on
the physical and mental health of the older people. However,
given advancements in medical care and increased life
expectancy, dementia has emerged as a significant concern
among the older ages. Therefore, we introduce cognitive
health as an additional indicator of health and examine the
relationship between these three aspects of old-age health.
Our findings reveal that the physical health of the old-age
affects their mental health, and both physical and mental
health have implications for cognitive health.
Second, to capture the unique characteristics of
Figure 3. The urban unemployment rate of the population aged from 16
to 24 (%) Chinese society, we incorporate household registration
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China (2023). (hukou [户口]) and political party membership as
two explanatory variables in our regression model to
The rapidly rising dependency ratio among the old-age reflect individuals’ socioeconomic status. We find that,
population and declining public support ratio (Figure 4) will compared to traditional measures such as education level
not only profoundly impact China’s economic growth but and place of residence, household registration type and
also put great pressure on the fragile social welfare system party membership not only significantly represent the
and scarce public health-care resources (Lee & Mason, 2011; socioeconomic status of the Chinese populace but also
United Nations, 2013). Government forecasts for medical exert a longer cumulative effect on the health status of the
and health-care financial burdens usually depend on the older people. These features specific to Chinese society
health indicators of older persons. Therefore, amid rapid may exacerbate health disparities among the older ages.
population aging, prioritizing the health status of the old-
age becomes paramount. In addition to health conditions The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Section
naturally deteriorating with age, many studies have indicated 2 reviews the literature on the relationship between health and
that socioeconomic status significantly affects the health socioeconomic status; Section 3 introduces the data used in
outcomes of the older adults. Therefore, this study aims to this study and provides a statistical description of the variables;
explore the influence of socioeconomic status on the health Section 4 presents the empirical results and summarizes the
of the older adults in China. The contributions of this study findings of this study; finally, in Section 5, we draw conclusions
are summarized as follows. regarding China’s future as a super-aged society.
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 86 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.2035