Page 82 - IJPS-11-5
P. 82
International Journal of
Population Studies Therapeutic resilience during COVID-19
2.2. Data analysis adopting practices such as wearing masks, avoiding eye
This researcher thoroughly examined all the written contact, and adhering to stay-at-home measures. They also
responses to find significant assertions made by preferred self-care remedies and expressed reluctance to
the participants. Subsequently, the responses were seek medical attention at hospitals, primarily due to their
systematically arranged and categorized using appropriate inherent distrust of such institutions.
labels that accurately represented the responses. During 2.3. Ethical permissions
this coding process, this researcher manually identified
the commonalities and contrasts evident in the texts. n receiving assurances on the protection of their data in
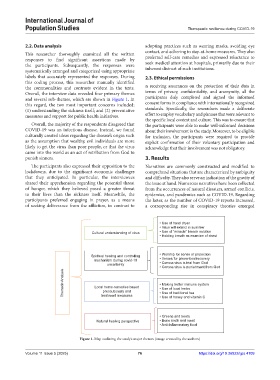
Overall, the interview data revealed four primary themes terms of privacy, confidentiality, and anonymity, all the
and several sub-themes, which are shown in Figure 1. In participants duly completed and signed the informed
this regard, the two most important concerns included: consent forms in compliance with internationally recognized
(1) understanding the sickness itself; and (2) preventative standards. Specifically, the researchers made a deliberate
measures and support for public health initiatives. effort to employ vocabulary and phrases that were relevant to
the specific local context and culture. This was to ensure that
Overall, the majority of the respondents disagreed that the participants were able to make well-informed decisions
COVID-19 was an infectious disease. Instead, we found about their involvement in the study. Moreover, to be eligible
culturally created ideas regarding the disease’s origin such for inclusion, the participants were required to provide
as the assumption that wealthy, evil individuals are more explicit confirmation of their voluntary participation and
likely to get the virus than poor people, or that the virus acknowledge that their involvement was not obligatory.
came into the world as an act of retribution from God to
punish sinners. 3. Results
The participants also expressed their opposition to the Narratives are commonly constructed and modified to
lockdowns, due to the significant economic challenges comprehend situations that are characterized by ambiguity
that they anticipated. In particular, the interviewees and difficulty. They also serve an indication of the gravity of
shared their apprehension regarding the potential threat the issue at hand. Numerous narratives have been collected
of hunger, which they believed posed a greater threat from the occurrences of natural disasters, armed conflicts,
to their lives than the sickness itself. Meanwhile, the epidemics, and pandemics such as COVID-19. Regarding
participants preferred engaging in prayer, as a means the latter, as the number of COVID-19 reports increased,
of seeking deliverance from the affliction, in contrast to a corresponding rise in conspiracy theories emerged
• Use of hand dryer
• Virus will extinct in summer
Cultural understanding of virus • Use of "miracle" bleach solution
• Holding breath as examine of chest
Spiritual healing and controlling • Worship for sense of protection
mechanism during covid-19 • Verses for prevention/recovery
uncertainty • Corona virus is trial from God
• Corona virus is punishment from God
Thematic Analysis Local home-remedies based • Making better immune system
• Use of local herbs
precautionary and
• Use of traditional tea
treatment measures
• Use of honey and vitamin C
• Greens and beets
Natural healing perspective • Bone broth and meat
• Anti-inflammatory food
Figure 1. Map outlining the study’s major themes (image created by the authors)
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 76 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.4109