Page 144 - IJPS-11-6
P. 144
International Journal of
Population Studies Social inclusion for refugees
Table 6. Composition of the first cluster Table 9. Comparative analysis of social integration factors
and refugee integration levels in Poland, Germany, and the
Members of Cluster 1 Average distance to the cluster center Czech Republic
Poland 0.393973
Indicator Poland Germany Czech Republic
Czech Republic 0.103242
Access to social 85 92 80
Spain 0.435879 services (%)
Social assistance 300 350 250
Table 7. Composition of the second cluster amount (€)
Access to integration 75 85 70
Members of Cluster 2 Average distance from the cluster center programs (%)
Bulgaria 0.08187732 Average age of 38 35 40
Italy 0.4254286 refugees (years)
Moldova 0.4137162 Youth share (15 – 35 45 50 40
Romania 0.09214597 years old) (%)
Higher education 30 40 25
level (%)
Table 8. Composition of the third cluster Length of stay (years) 2 3 1.5
Members of Cluster 3 Average distance from the cluster center Language proficiency 3 4 3
Germany 0.507379 level (scale 1 – 5)
Great Britain 0.507379 Employment rate (%) 60 70 55
Participation in 65 75 55
community life (%)
analysis due to their representativeness and strategic Language proficiency 70 80 65
relevance. These countries play a key role in responding (%)
to refugee flows from Ukraine and exhibit moderate yet Social cohesion 0.6 0.8 0.5
improving integration policies, offering valuable insights (index)
into practical solutions within resource-limited settings. Integration level 0.7 0.85 0.65
As a leader in advanced integration policies, Germany – (index)
from Cluster 3 – serves as a benchmark for best practices.
Its approach to long-term refugee integration offers a
valuable example for other host countries. By focusing support integration, show room for improvement in their
on these selected countries, the analysis captures a range social support systems.
of integration policy levels, providing a comprehensive Key findings from the analysis highlight significant
perspective on the challenges and opportunities of refugee disparities in refugee integration across host countries.
integration across Europe. Germany demonstrates strong performance, with higher
integration levels attributed to its well-developed social
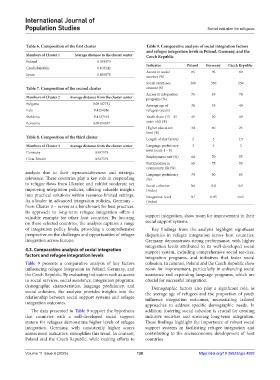
4.3. Comparative analysis of social integration support system, including comprehensive social services,
factors and refugee integration levels integration programs, and initiatives that foster social
Table 9 presents a comparative analysis of key factors cohesion. In contrast, Poland and the Czech Republic show
influencing refugee integration in Poland, Germany, and room for improvement, particularly in enhancing social
the Czech Republic. By evaluating indicators such as access assistance and expanding language programs, which are
to social services, social assistance, integration programs, crucial for successful integration.
demographic characteristics, language proficiency, and Demographic factors also play a significant role, as
social cohesion, the analysis provides insights into the the average age of refugees and the proportion of youth
relationship between social support systems and refugee influence integration outcomes, necessitating tailored
integration outcomes. approaches to address specific demographic needs. In
The data presented in Table 9 support the hypothesis addition, fostering social cohesion is crucial for creating
that countries with a well-developed social support inclusive societies and ensuring long-term integration.
system for refugees demonstrate higher levels of refugee These findings highlight the importance of robust social
integration. Germany, with consistently higher scores support systems in facilitating refugee integration and
across most indicators, exemplifies this trend. In contrast, contributing to the socioeconomic development of host
Poland and the Czech Republic, while making efforts to countries.
Volume 11 Issue 6 (2025) 138 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.4502