Page 12 - IJPS-5-1
P. 12
Language and self-assessed health in the U.S
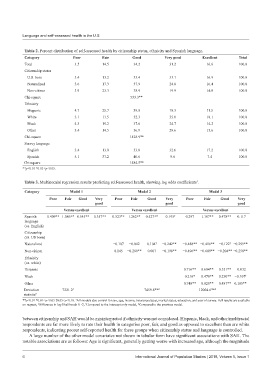
Table 2. Percent distribution of self-assessed health by citizenship status, ethnicity and Spanish language.
Category Poor Fair Good Very good Excellent Total
Total 3.5 14.5 34.2 31.2 16.6 100.0
Citizenship status
U.S. born 3.4 13.2 33.4 33.1 16.9 100.0
Naturalized 3.6 17.3 37.9 24.8 16.4 100.0
Non-citizen 3.9 23.3 38.9 19.9 14.0 100.0
Chi-square 533.3**
Ethnicity
Hispanic 4.7 25.7 39.8 18.3 11.5 100.0
White 3.1 11.5 32.3 35.0 18.1 100.0
Black 4.3 19.2 37.6 24.7 14.2 100.0
Other 3.4 14.5 36.9 29.6 15.6 100.0
Chi-square 1428.9**
Survey language
English 3.4 13.0 33.8 32.6 17.2 100.0
Spanish 5.1 37.2 40.6 9.6 7.4 100.0
Chi-square 1484.5**
**p<0.01 *0.01<p<0.05.
Table 3. Multinomial regression results predicting self-assessed health, showing log odds coefficients .
1
Category Model 1 Model 2 Model 3
Poor Fair Good Very Poor Fair Good Very Poor Fair Good Very
good good good
Versus excellent Versus excellent Versus excellent
Spanish 0.409** 1.086** 0.545** −0.357** 0.523** 1.262** 0.527** −0.195 † 0.297 1.187** 0.478** −0.117
language
(vs. English)
Citizenship
(vs. US born)
Naturalized −0.107 −0.042 0.104 † −0.242** −0.488** −0.416** −0.122 −0.299**
†
Non-citizen 0.145 −0.269** 0.007 −0.198** −0.496** −0.609** −0.204** −0.258**
Ethnicity
(vs. white)
Hispanic 0.716** 0.604** 0.351** −0.032
Black 0.216* 0.478** 0.230** −0.107 †
Other 0.748** 0.820** 0.487** 0.185**
Deviation 7221.2 3 7459.8** 4 12004.6** 4
statistic 2
**p<0.01 *0.01<p<0.05 †0.05<p<0.10. All models also control for sex, age, income, insurance status, marital status, education, and year of survey. Full results are available
1
on request, Difference in log-likelihoods X -2, Compared to the intercept only model, Compared to the previous model.
3
4
2
between citizenship and SAH would be misinterpreted if ethnicity was not considered. Hispanic, black, and other/multiracial
respondents are far more likely to rate their health in categories poor, fair, and good as opposed to excellent than are white
respondents, indicating poorer self-reported health for these groups when citizenship status and language is controlled.
A large number of the other model covariates not shown in tabular form have significant associations with SAH. The
notable associations are as follows: Age is significant, generally getting worse with increased age, although the magnitude
6 International Journal of Population Studies | 2019, Volume 5, Issue 1