Page 49 - IJPS-9-2
P. 49
International Journal of
Population Studies Professional quality of life – a mediation model
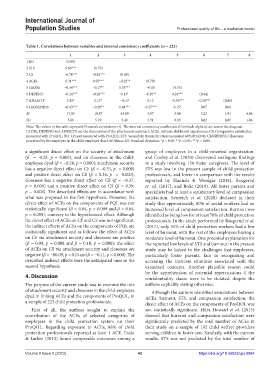
Table 1. Correlations between variables and internal consistency coefficients (n = 223)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 BO (0.80)
2 STS 0.66*** (0.73)
3 CS −0.76*** −0.42*** (0.88)
4 ACEs 0.31*** 0.26*** −0.22** (0.79)
5 CLOSE −0.34*** −0.17** 0.35*** −0.10 (0.53)
6 DEPEND −0.24*** −0.26*** 0.13* −0.20** 0.24*** (0.44)
7 ANXIETY 0.15* 0.17* −0.13 0.12 −0.39*** −0.38*** (0.86)
8 CLOSENESS −0.43*** −0.20** 0.41*** −0.27*** 0.15* 0.07 0.06 -
M 17.85 19.87 43.09 2.87 3.84 3.22 1.91 4.84
SD 5.66 5.29 5.40 2.31 0.63 0.62 0.85 1.04
Note: The values in the table represent Pearson’s correlations (r). The internal consistency coefficients (Cronbach alpha α) are across the diagonal.
CLOSE, DEPEND and ANXIETY are the dimensions of the attachment construct; ACEs: Adverse childhood experiences; CS: Compassion satisfaction
measured with ProQOL; BO: Urnout measured with ProQOL; STS: Secondary traumatic stress measured with ProQOL; CLOSENESS: Closeness
perceived by the employee in the child-employee dyad; M: Mean; SD: Standard deviation. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001
a significant direct effect on the security of attachment group of employees in a child-oriented organization,
(β = -0.25, p = 0.003), and on closeness in the child- and Cooley et al. (2020) discovered analogous findings
employee dyad (β = −0.28, p = 0.000); attachment security in a study involving 150 foster caregivers. The level of
has a negative direct effect on CF (β = −0.34, p = 0.000) STS was low in the present sample of child protection
and positive direct effect on CS (β = 0.34, p = 0.000); professionals, and lower in comparison with the results
closeness has a negative direct effect on CF (β = −0.37, reported by Hannah & Woolgar (2018), Baugerud
p = 0.000) and a positive direct effect on CS (β = 0.39, et al. (2017), and Bolic (2019). All foster parents and
p = 0.000). The described effects are in accordance with specialists had at least a satisfactory level of compassion
what was proposed in the first hypothesis. However, the satisfaction. Senreich et al. (2020) declared in their
direct effect of ACEs on the components of PQL was not study that approximately 60% of social workers had an
statistically significant (β = 0.04, p = 0.099 and β = 0.04, increased level of compassion satisfaction. Burnout was
p = 0.099), contrary to the hypothesized effect. Although identified as being low for at least 70% of child protection
the direct effect of ACEs on CF and CS was not significant, professionals. In the study performed by Baugerud et al.
the indirect effects of ACEs on the components of PQL are (2017), only 31% of child protection workers had a low
statistically significant and as follows: the effect of ACEs level of burnout, with the rest of the employees having a
on CF via attachment security and closeness are positive moderate level of burnout. One potential explanation for
(β = 0.09, p = 0.008 and β = 0.10, p = 0.000); the effect the reported low levels of STS and burnout in the present
of ACEs on CS via attachment security and closeness are study may be linked to the challenges that employees,
negative (β = −00.09, p =.010 and β = −0.11, p = 0.000). The particularly foster parents, face in recognizing and
described indirect effects were the anticipated ones in the accessing the intricate emotions associated with the
second hypothesis. examined concepts. Another plausible reason could
be the apprehension of potential repercussions if the
4. Discussion confidentiality clause were to be violated, despite the
The purpose of the current study was to examine the role authors explicitly stating otherwise.
of attachment security and closeness in the child-employee Although the authors identified associations between
dyad in linking ACEs and the components of ProQOL, in ACEs, burnout, STS, and compassion satisfaction, the
a sample of 223 child protection professionals. direct effect of ACEs on the components of ProQOL was
First of all, the authors sought to explain the not statistically significant. Hiles Howard et al. (2015)
contribution of the ACEs of selected categories of showed that burnout and compassion satisfaction were
employees in the child protection system on their significantly predicted by the total number of ACEs in
ProQOL. Regarding exposure to ACEs, 88% of child their study on a sample of 192 child welfare providers
protection professionals reported at least 1 ACE. Esaki serving children in foster care. Similarly, with the current
& Larkin (2013) found comparable outcomes among a results, STS was not predicted by the total number of
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 43 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.0884