Page 10 - IMO-2-1
P. 10
Innovative Medicines & Omics Incretin mimetics in diabetes management
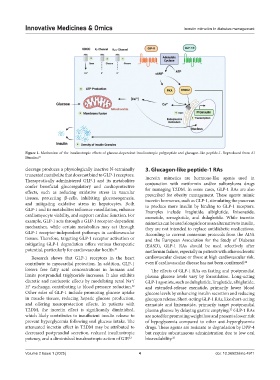
Figure 1. Mechanism of the insulinotropic effects of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1. Reproduced from Al
Musaimi 12
cleavage produces a physiologically inactive N-terminally 3. Glucagon-like peptide-1 RAs
truncated metabolite that does not bind to GLP-1 receptors. Incretin mimetics are hormone-like agents used in
Therapeutically administered GLP-1 and its metabolites conjunction with metformin and/or sulfonylurea drugs
confer beneficial glucoregulatory and cardioprotective for managing T2DM. In some cases, GLP-1 RAs are also
effects, such as reducing oxidative stress in vascular prescribed for obesity management. These agents mimic
tissues, protecting β-cells, inhibiting gluconeogenesis, incretin hormones, such as GLP-1, stimulating the pancreas
and mitigating oxidative stress in hepatocytes. Both to produce more insulin by binding to GLP-1 receptors.
GLP-1 and its metabolites influence vasodilation, enhance Examples include liraglutide, albiglutide, lixisenatide,
cardiomyocyte viability, and support cardiac function. For exenatide, semaglutide, and dulaglutide. While incretin
example, GLP-1 acts through a GLP-1 receptor-dependent mimetics can be used alongside or as an alternative to insulin,
mechanism, while certain metabolites may act through they are not intended to replace antidiabetic medications.
GLP-1 receptor-independent pathways in cardiovascular According to current consensus protocols from the ADA
tissues. Therefore, targeting GLP-1 receptor activation or and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes
mitigating GLP-1 degradation offers various therapeutic (EASD), GLP-1 RAs should be used selectively after
potential, particularly for cardiovascular health. 21 metformin failure, especially in patients with atherosclerotic
Research shows that GLP-1 receptors in the heart cardiovascular disease or those at high cardiovascular risk,
contribute to myocardial protection. In addition, GLP-1 even if cardiovascular disease has not been confirmed. 24
lowers free fatty acid concentrations in humans and The effects of GLP-1 RAs on fasting and postprandial
limits postprandial triglyceride increases. It also exhibits plasma glucose levels vary by formulation. Long-acting
diuretic and natriuretic effects by modulating renal Na / GLP-1 agonists, such as dulaglutide, liraglutide, albiglutide,
+
H exchange, contributing to blood pressure reduction. and extended-release exenatide, primarily lower blood
+
22
Other roles of GLP-1 include promoting glucose uptake glucose levels by enhancing insulin secretion and reducing
in muscle tissues, reducing hepatic glucose production, glucagon release. Short-acting GLP-1 RAs, like short-acting
and offering neuroprotection effects. In patients with exenatide and lixisenatide, primarily target postprandial
T2DM, the incretin effect is significantly diminished, plasma glucose by delaying gastric emptying. GLP-1 RAs
25
which likely contributes to insufficient insulin release to are noted for promoting weight loss and present a lower risk
prevent hyperglycemia following oral glucose intake. The of hypoglycemia compared to other anti-hyperglycemic
attenuated incretin effect in T2DM may be attributed to drugs. These agents are resistant to degradation by DPP-4
decreased postprandial secretion, reduced insulinotropic but require subcutaneous administration due to low oral
potency, and a diminished insulinotropic action of GIP. 23 bioavailability. 26
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/imo.4911