Page 44 - IMO-2-1
P. 44
Innovative Medicines & Omics Current approach in the management of kidney disease
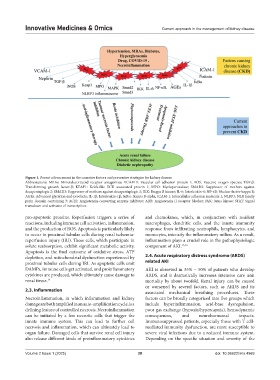
Figure 1. Recent advancement in the causative factors and preventive strategies for kidney disease
Abbreviations: MRAs: Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion protein 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TGF-β:
Transforming growth factor-β; KEAP1: Kelch-like ECH associated protein 1; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; SMAD2: Suppressor of mothers against
decapentaplegic 2; SMAD3: Suppressor of mothers against decapentaplegic 3; IKK: Ikappa B kinase; IL-6: Interleukin-6; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B;
AGEs: Advanced glycation end-products; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; IκBα: Ikappa B-alpha; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule 1; NLRP3: NLR family
pyrin domain containing 3; ACEI: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB: Angiotensin II receptor blocker; JAK: Janus kinase; STAT: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription.
pro-apoptotic proteins. Reperfusion triggers a series of and chemokines, which, in conjunction with resident
reactions, including immune cell activation, inflammation, macrophages, dendritic cells, and the innate immunity
and the production of ROS. Apoptosis is particularly likely response from infiltrating neutrophils, lymphocytes, and
to occur in proximal tubular cells during renal ischemia- monocytes, intensify the inflammatory milieu. As a result,
reperfusion injury (IRI). These cells, which participate in inflammation plays a crucial role in the pathophysiologic
solute reabsorption, exhibit significant metabolic activity. component of AKI. 15,16
Apoptosis is the final outcome of oxidative stress, ATP
depletion, and mitochondrial dysfunction experienced by 2.4. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
proximal tubular cells during IRI. As apoptotic cells emit related AKI
DAMPs, immune cells get activated, and proinflammatory AKI is observed in 35% – 50% of patients who develop
cytokines are produced, which ultimately cause damage to ARDS, and it dramatically increases intensive care unit
renal tissue. 14 mortality by about twofold. Renal injury can be caused
or worsened by several factors, such as ARDS and its
2.3. Inflammation associated mechanical breathing procedures. These
Necroinflammation, in which inflammation and kidney factors can be broadly categorized into five groups which
damage are both amplified in an auto-amplification cycle, is a include hyperinflammation, acid-base dysregulation,
defining feature of controlled necrosis. Necroinflammation poor gas exchange (hypoxia/hypercapnia), hemodynamic
can be initiated by a few necrotic cells that trigger the consequences, and neurohormonal impacts.
innate immune system. This can lead to further cell Immunosuppressed patients, especially those with T cell-
necrosis and inflammation, which can ultimately lead to mediated immunity dysfunction, are more susceptible to
organ failure. Damaged cells that survive renal cell injury severe viral infections due to a reduced immune system.
also release different kinds of proinflammatory cytokines Depending on the specific situation and severity of the
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 38 doi: 10.36922/imo.4969