Page 24 - IMO-2-3
P. 24
Innovative Medicines & Omics Progress in antivenom therapy
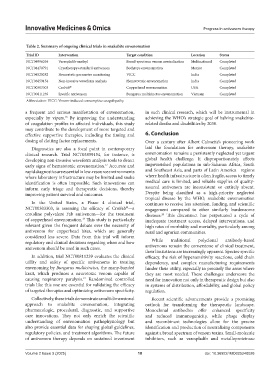
Table 2. Summary of ongoing clinical trials in snakebite envenomation
Trial ID Intervention Target condition Location Status
NCT04996264 Varespladib-methyl Broad-spectrum venom neutralization Multinational Completed
NCT04470791 Cryotherapy+standard antivenom Bothrops envenomation Mexico Completed
NCT04520282 Hemostatic parameter monitoring VICC India Completed
NCT03859154 Non-invasive waveform analysis Hematotoxic envenomation India Completed
NCT00303303 CroFab ® Copperhead envenomation USA Completed
NCT00811239 Specific antivenom Bungarus multicinctus envenomation Vietnam Completed
Abbreviation: VICC: Venom-induced consumptive coagulopathy.
a frequent and serious manifestation of envenomation, in such clinical research, which will be instrumental in
especially by vipers. By improving the understanding achieving the WHO’s strategic goal of halving snakebite-
16
of coagulation profiles in affected individuals, this study related deaths and disabilities by 2030.
may contribute to the development of more targeted and
effective supportive therapies, including the timing and 6. Conclusion
dosing of clotting factor replacements. Over a century after Albert Calmette’s pioneering work
Diagnostics are also a focal point in contemporary laid the foundation for antivenom therapy, snakebite
clinical research. Trial NCT03859154, for instance, is envenomation remains a persistently neglected yet urgent
developing non-invasive waveform analysis tools to detect global health challenge. It disproportionately affects
early signs of hematotoxic envenomation. Accurate and impoverished populations in sub-Saharan Africa, South
17
rapid diagnostics are essential in low-resource environments and Southeast Asia, and parts of Latin America—regions
where laboratory infrastructure may be limited and snake where health infrastructure is often fragile, access to timely
identification is often impossible. Such innovations can medical care is limited, and reliable supplies of quality-
inform early triage and therapeutic decisions, thereby assured antivenom are inconsistent or entirely absent.
improving patient survival and outcomes. Despite being classified as a high-priority neglected
tropical disease by the WHO, snakebite envenomation
In the United States, a Phase 4 clinical trial, continues to receive less attention, funding, and scientific
NCT00303303, is assessing the efficacy of CroFab —a engagement compared to other similarly burdensome
®
crotaline polyvalent Fab antivenom—for the treatment diseases. This disconnect has perpetuated a cycle of
20
of copperhead envenomation. This study is particularly inadequate treatment access, delayed interventions, and
18
relevant given the frequent debate over the necessity of high rates of morbidity and mortality, particularly among
antivenom for copperhead bites, which are generally rural and agrarian communities.
considered less severe. Data from this trial will inform
regulatory and clinical decisions regarding when and how While traditional polyclonal antibody-based
antivenom should be used in such cases. antivenoms remain the cornerstone of clinical treatment,
their limitations are increasingly apparent. Species-specific
In addition, trial NCT00811239 evaluates the clinical efficacy, the risk of hypersensitivity reactions, cold chain
utility and safety of specific antivenoms in treating dependency, and complex manufacturing requirements
envenoming by Bungarus multicinctus, the many-banded hinder their utility, especially in precisely the areas where
krait, which produces a neurotoxic venom capable of they are most needed. These challenges underscore the
19
causing respiratory paralysis. Randomized controlled need for innovation not only in therapeutic design but also
trials like this one are essential for validating the efficacy in systems of distribution, affordability, and global policy
of targeted therapies and optimizing antivenom specificity. regulation.
Collectively, these trials demonstrate a multidimensional Recent scientific advancements provide a promising
approach to snakebite envenomation, integrating outlook for transforming the therapeutic landscape.
pharmacologic, procedural, diagnostic, and supportive Monoclonal antibodies offer enhanced specificity
care innovations. They not only enrich the scientific and reduced immunogenicity, while phage display
understanding of envenomation pathophysiology but and recombinant technologies allow for the precise
also provide essential data for shaping global guidelines, identification and production of neutralizing components
regulatory policies, and treatment algorithms. The future against a broad spectrum of venom toxins. Small-molecule
of antivenom therapy depends on sustained investment inhibitors, such as varespladib and metalloproteinase
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 18 doi: 10.36922/IMO025240026