Page 15 - ITPS-6-2
P. 15
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Theranostics in neurosurgery
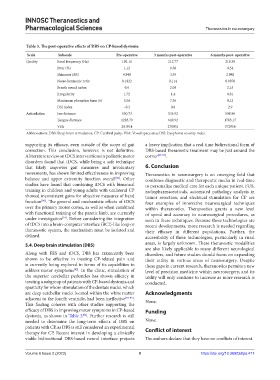
Table 3. The post‑operative effects of DBS on CP‑based dystonia
Scale Subscale Pre‑operative 3 months post‑operative 6 months post‑ operative
Quality Basal frequency (Hz) 192.11 212.77 219.38
Jitter (%) 1.12 0.58 0.54
Shimmer (dB) 4.948 3.39 2.988
Noise-harmonic ratio 0.1822 0.114 0.0878
Breath sound index 0.6 2.08 2.15
Irregularity 1.72 1.4 0.81
Maximum phonation time (s) 3.56 7.36 9.12
DSI index –0.2 0.8 2.9
Articulation Jaw distance 550.73 535.92 508.96
Tongue distance 1283.79 649.92 1783.17
VSA 281914 278951 372958
Abbreviations: DBS: Deep brain stimulation; CP: Cerebral palsy; VSA: Vowel space area; DSI: Dysphonia severity index.
supporting its efficacy, even outside of the scope of gait a heavy implication that a real-time bidirectional form of
correction. This conclusion, however, is not definitive. DBS-based theranostic treatment may be just around the
A literature review on tDCS interventions in pediatric motor corner [97-99] .
disorders found that tDCS, while being a safe technique
that likely improves gait measures and involuntary 6. Conclusion
movements, has shown limited effectiveness in improving Theranostics in neurosurgery is an emerging field that
balance and upper extremity function overall . Other combines diagnostic and therapeutic media in real-time
[86]
studies have found that combining tDCS with bimanual to personalize medical care for each unique patient. FUS,
training in children and young adults with unilateral CP radiopharmaceuticals, automated pathology analysis in
showed inconsistent gains for objective measures of hand tumor resection, and electrical stimulation for CP are
[90]
function . The general and mechanistic effects of tDCS four examples of innovative neurosurgical techniques
over the primary motor cortex, as well as when combined within theranostics. Theranostics grants a new level
with functional training of the paretic limb, are currently of speed and accuracy to neurosurgical procedures, as
under investigation . Before considering the integration seen in these techniques. Because these technologies are
[91]
of tDCS into a brain-computer interface (BCI)-like loop or recent developments, more research is needed regarding
theranostic system, the mechanism must be isolated and their efficacy in different populations. Further, the
defined. accessibility of these technologies, particularly in rural
5.4. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) areas, is largely unknown. These theranostic modalities
are also likely applicable to many different neurological
Along with FES and tDCS, DBS has rxxxecently been disorders, and future studies should focus on expanding
shown to be effective in treating CP-related pain and their utility in various areas of neurosurgery. Despite
is currently being explored in terms of its capabilities to these gaps in current research, theranostics permits a new
address motor symptoms . In the clinic, stimulation of level of precision medicine within neurosurgery, and its
[92]
the superior cerebellar peduncles has shown efficacy in utility will only continue to increase as more research is
treating a subgroup of patients with CP-based dystonia and conducted.
spasticity for whom stimulation of the dentate nuclei, which
are deep cerebellar nuclei located within the white matter Acknowledgments
adjacent to the fourth ventricle, had been ineffective [93-95] . None.
This finding coheres with other studies supporting the
efficacy of DBS in improving motor symptoms in CP-based Funding
dystonia, as shown in Table 3 . Further research is still
[96]
needed to determine the long-term effects of DBS on None.
patients with CP, as DBS is still considered an experimental Conflict of interest
therapy for CP. Recent interest in developing a clinically
viable bidirectional DBS-based neural interface projects The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Volume 6 Issue 2 (2023) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.417