Page 13 - ITPS-7-1
P. 13
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Liquid biopsy and digital PCR in cancer
remain negative since they require around 10 cells to be 6. Strengths and limitations of LB
9
clinically detectable, and the patient probably does not
show clinical signs or symptoms of this incipient relapse. Due to the reproducibility, high sensitivity and high
specificity of the method, LB constitutes a tool of great
In this way, a positive LB result achieves a significant
diagnostic anticipation of the presence of a primary tumor, diagnostic and therapeutic indication value in cancer. Its
and allows both monitoring of therapeutic efficacy and main advantage is that it can be applied as many times
as necessary, and that it can be quantifiable, serving as
early detection of the emergence of resistant variants [39-41] a parameter for monitoring the therapeutic evolution of
(Figure 6). Today, LB is being applied to the detection of a tumor, and for detecting its mutational changes that
most tumors, and the use of gene panels provides extensive require modifications in the treatment strategy. In this
information on the genetic fingerprint of each tumor, with way, it plays a role in the monitoring of minimal residual
high levels of sensitivity and specificity.
disease.
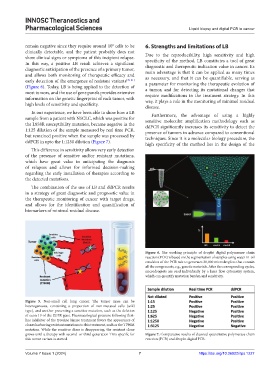
In our experience, we have been able to show how a LB Furthermore, the advantage of using a highly
sample from a patient with NSCLC, which was positive for sensitive molecular amplification methodology such as
the L858R susceptibility mutation, became negative in the ddPCR significantly increases its sensitivity to detect the
1:125 dilution of the sample measured by real time PCR, presence of tumors in advance compared to conventional
but remained positive when the sample was processed by techniques. Since it is a molecular biology procedure, the
ddPCR in upto the 1:1250 dilution (Figure 7).
high specificity of the method lies in the design of the
This difference in sensitivity allows very early detection
of the presence of sensitive and/or resistant mutations,
which have great value in anticipating the diagnosis
of relapses and allows for informed decision-making
regarding the early installation of therapies according to
the detected mutations.
The combination of the use of LB and ddPCR results
in a strategy of great diagnostic and prognostic value in
the therapeutic monitoring of cancer with target drugs,
and allows for the identification and quantification of
biomarkers of minimal residual disease.
Figure 6. The working principle of droplet digital polymerase chain
reaction (PCR) is based on the segmentation of samples using water-in-oil
emulsion of the PCR mix to generates 20,000 microdroplets that contain
all the components, e.g., genetic materials. After the corresponding cycles,
microdroplets are read individually by a laser flow cytometry system,
which can quantify mutation burden and sensitivity.
Figure 5. Non-small cell lung cancer. The tumor mass can be
heterogeneous, containing a proportion of non-mutated cells (wild
type), and another presenting a sensitive mutation, such as the deletion
of exon 19 of the EGFR gene. Pharmacological pressure following first-
line inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase treatment favors the appearance of
clones harboring resistant mutations to this treatment, such as the T790M
mutation. While the sensitive clone is disappearing, the resistant clone
grows until a therapy with second- or third-generation TKIs specific for Figure 7. Comparative results of classical quantitative polymerase chain
this tumor variant is started. reaction (PCR) and droplet digital PCR.
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.1227