Page 144 - ITPS-7-2
P. 144
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Dapsone enhance skin flap survival
and, therefore, the production of free radicals and
additional apoptosis. 36,40 Moreover, experimental studies of
I/R injury have revealed that TNF-α is a key component of
inflammation-mediated neutrophil migration, activation,
and, consequently, the progression of the inflammatory
response. 41-43 Expression of TNF-α not only leads to
more cumulative apoptosis following I/R injury but also
potentially enhances the expression of adhesion markers,
chemokines, and cytokines, which lead to more infiltration
of neutrophils into the injured site. 44
On the other hand, the application of dapsone has
exhibited anti-inflammatory properties over recent
decades. Conventionally, dapsone is well-known for its
anti-microbial and anti-protozoa effects. However, its
clinical application in autoimmune settings has spurred
the exploration of anti-inflammatory properties targeting
both molecular and cellular elements of inflammation.
45
Indeed, the potential of dapsone to affect specific elements
of inflammation led us to formulate our hypothesis.
Modschiedler et al. have the first to conclude that dapsone
could suppress the adhesion of neutrophils to epidermal
binding sites. Subsequent research revealed that dapsone
46
not only inhibits the chemotaxis of neutrophils but also
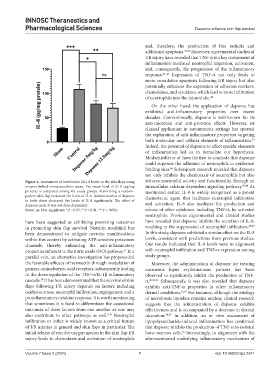
Figure 4. Assessment of interleukin (IL)-8 levels in the skin flaps using reduces neutrophil activity and functionality through an
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The mean level of IL-8 (pg/mg intracellular calcium-dependent signaling pathway. 47,48 As
protein) is compared among the study groups. Performing a random- mentioned earlier, IL-8 is widely recognized as a potent
pattern skin flap increased the levels of IL-8. Administration of dapsone chemotactic agent that facilitates neutrophil infiltration
in both doses decreased the levels of IL-8 significantly. The effect of
dapsone on IL-8 was not dose-dependent. and activation. IL-8 also mediates the production and
Notes: ns: Non-significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. release of other cytokines, including TNF-α, by activated
neutrophils. Previous experimental and clinical studies
have been suggested as exhibiting promising outcomes have revealed that dapsone inhibits the secretion of IL-8,
in promoting skin flap survival. Notably, modafinil has resulting in the suppression of neutrophil infiltration. 44,49
been demonstrated to mitigate necrotic manifestations In this study, dapsone exhibited a similar effect on the IL-8
within this context by activating ATP-sensitive potassium levels, consistent with predictions from previous studies.
channels, thereby enhancing the anti-inflammatory Our results indicated that IL-8 levels were in alignment
properties inherent to the nitric oxide (NO) pathway. In a with neutrophil infiltration and TNF-α expression among
37
parallel vein, an alternative investigation has propounded study groups.
the favorable efficacy of ivermectin through modulation of Moreover, the administration of dapsone for treating
gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors, subsequently leading cutaneous lupus erythematosus patients has been
to the downregulation of the TNF-α/IL-1β inflammatory observed to significantly inhibit the production of TNF-
cascade. It has been demonstrated that the survival of skin α. 29,50,51 Subsequently, it was also revealed that dapsone
38
flaps following I/R injury depends on factors including exhibits anti-TNF-α properties in other inflammatory
oxidative stress, neutrophil infiltration, angiogenesis, and a dermal conditions. 52,53 For instance, although the etiology
proinflammatory cytokine response. It is worth mentioning of necrobiosis lipoidica remains unclear, clinical research
that sometimes it is hard to differentiate the causational suggests that the administration of dapsone exhibits
outcomes of these factors from one another as one may effectiveness and is accompanied by a decrease in dermal
also contribute to other pathways as well. Neutrophil ulceration. 54,55 In addition, an in vitro assessment of
9,39
infiltration or influx is widely known as a critical feature lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation has confirmed
of I/R injuries in general and skin flaps in particular. The that dapsone inhibits the production of TNF-α in isolated
initial release of reactive oxygen species in the skin flap I/R bone marrow cells. Interestingly, in alignment with the
56
injury leads to chemotaxis and activation of neutrophils aforementioned underlying inflammatory mechanism of
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/itps.2241