Page 145 - ITPS-7-2
P. 145
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Dapsone enhance skin flap survival
A
B
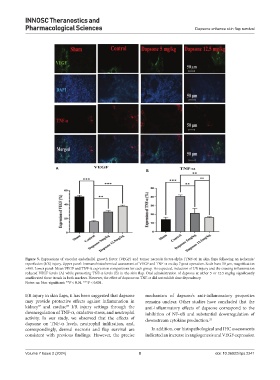
Figure 5. Expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in skin flaps following an ischemia/
reperfusion (I/R) injury. Upper panel: Immunohistochemical assessment of VEGF and TNF-α on day 7 post-operation. Scale bars: 50 µm, magnification
×400. Lower panel: Mean VEGF and TNF-α expression comparisons for each group. As expected, induction of I/R injury and the ensuing inflammation
reduced VEGF levels (A) while promoting TNF-α levels (B) in the skin flap. Oral administration of dapsone at either 5 or 12.5 mg/kg significantly
ameliorated these trends in both markers. However, the effect of dapsone on TNF-α did not exhibit dose dependency.
Notes: ns: Non-significant; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
I/R injury in skin flaps, it has been suggested that dapsone mechanism of dapsone’s anti-inflammatory properties
may provide protective effects against inflammation in remains unclear. Other studies have concluded that the
kidney and cardiac I/R injury settings through the anti-inflammatory effects of dapsone correspond to the
58
57
downregulation of TNF-α, oxidative stress, and neutrophil inhibition of NF-κB and substantial downregulation of
activity. In our study, we observed that the effects of downstream cytokine production. 32
dapsone on TNF-α levels, neutrophil infiltration, and,
correspondingly, dermal necrosis and flap survival are In addition, our histopathological and IHC assessments
consistent with previous findings. However, the precise indicated an increase in angiogenesis and VEGF expression
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2024) 8 doi: 10.36922/itps.2241