Page 143 - ITPS-7-2
P. 143
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Dapsone enhance skin flap survival
A B
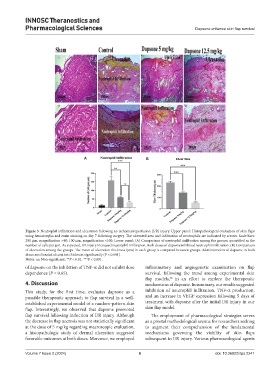
Figure 3. Neutrophil infiltration and ulceration following an ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Upper panel: Histopathological evaluation of skin flaps
using hematoxylin and eosin staining on day 7 following surgery. The ulcerated area and infiltration of neutrophils are indicated by arrows. Scale bars:
200 µm, magnification ×40; 100 µm, magnification ×100. Lower panel: (A) Comparison of neutrophil infiltration among the groups, quantified as the
number of cells per µm. As expected, I/R injury increased neutrophil infiltration. Both doses of dapsone inhibited neutrophil infiltration. (B) Comparison
of ulceration among the groups. The mean of ulceration thickness (µm) in each group is compared between groups. Administration of dapsone in both
doses ameliorated ulceration thickness significantly (P < 0.001).
Notes: ns: Non-significant; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
of dapsone on the inhibition of TNF-α did not exhibit dose inflammatory and angiogenetic examination on flap
dependence (P = 0.65). survival, following the trend among experimental skin
flap models, in an effort to explore the therapeutic
36
4. Discussion mechanisms of dapsone. In summary, our results suggested
This study, for the first time, evaluates dapsone as a inhibition of neutrophil infiltration, TNF-α production,
possible therapeutic approach to flap survival in a well- and an increase in VEGF expression following 5 days of
established experimental model of a random-pattern skin treatment with dapsone after the initial I/R injury in our
flap. Interestingly, we observed that dapsone promoted skin flap model.
flap survival following induction of I/R injury. Although The employment of pharmacological strategies serves
the decrease in flap necrosis was not statistically significant as a pivotal methodological avenue for researchers seeking
at the dose of 5 mg/kg regarding macroscopic evaluation, to augment their comprehension of the fundamental
a histopathologic study of dermal ulceration suggested mechanisms governing the viability of skin flaps
favorable outcomes at both doses. Moreover, we employed subsequent to I/R injury. Various pharmacological agents
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/itps.2241