Page 64 - ITPS-7-2
P. 64
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Youth brain health check and dysregulation
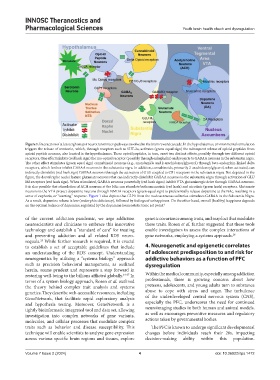
Figure 1. Interaction of at least eight major neurotransmitter-pathways involved in the brain reward cascade. In the hypothalamus, environmental stimulation
triggers the release of serotonin, which, through receptors such as 5HT-2a, activates (green equal sign) the subsequent release of opioid peptides from
opioid peptide neurons, also located in the hypothalamus. These opioid peptides, in turn, exert two distinct effects, possibly through two different opioid
receptors. One effect inhibits (red hash sign) the mu-opioid receptor (possibly through enkephalin) and projects to GABAA neurons in the substantia nigra.
The other effect stimulates (green equal sign) cannabinoid neurons (e.g., anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol) through beta-endorphin-linked delta
receptors, which further inhibit GABAA neurons in the substantia nigra. In addition, cannabinoids, primarily 2-arachidonoylglycerol, when activated, can
indirectly disinhibit (red hash sign) GABAA neurons through the activation of G1/0 coupled to CB1 receptors in the substantia nigra. Not depicted in the
figure, the dorsal raphe nuclei feature glutamate neurons that can indirectly disinhibit GABAA neurons in the substantia nigra through activation of GLU
M3 receptors (red hash sign). When stimulated, GABAA neurons powerfully (red hash signs) inhibit VTA glutaminergic drive through GABAA neurons.
It is also possible that stimulation of ACH neurons at the NAc can stimulate both muscarinic (red hash) and nicotinic (green hash) receptors. Glutamate
neurons in the VTA project dopamine neurons through NMDA receptors (green equal sign) to preferentially release dopamine at the NAc, resulting in a
sense of euphoria, or “wanting” response. Figure 1 also depicts that GLP1 from the nucleus tractus solitarius stimulates GABAA in the Substantia Nigra.
As a result, dopamine release is low (endorphin deficiency), followed by feelings of unhappiness. On the other hand, overall (healthy) happiness depends
on the optimal balance of dopamine, regulated by the dopamine homeostatic tonic set point. 6
of the current addiction pandemic, we urge addiction genetic covariance among traits, and map loci that modulate
neuroscientists and clinicians to embrace this innovative these traits. Rosen et al. further suggested that these tools
technology and establish a “standard of care” for treating enable investigators to assess the complex interactions of
and preventing addiction and all related RDS neuro- gene networks, employing a systems approach. 28
sequala. While further research is required, it is crucial
23
to establish a set of acceptable guidelines that include 4. Neurogenetic and epigenetic correlates
an understanding of the RDS concept. Understanding of adolescent predisposition to and risk for
neurogenetics by utilizing a “systems biology” approach addictive behaviors as a function of PFC
such as precision behavioral management, as outlined dysregulation
herein, seems prudent and represents a step forward in
restoring well-being to the billions afflicted globally. 24-27 In Within the medical community, especially among addiction
terms of a system biology approach, Rosen et al. outlined professionals, there is growing concern about how
the theory behind complex trait analysis and systems preteens, adolescents, and young adults turn to substance
genetics. They describe web-accessible resources, including abuse to cope with stress and anger. The turbulence
GeneNetwork, that facilitate rapid exploratory analysis of the underdeveloped central nervous system (CNS),
and hypothesis testing. Moreover, GeneNetwork is a especially the PFC, underscores the need for continued
tightly bioinformatic integrated tool and data set, allowing neuroimaging studies in both human and animal models,
investigation into complex networks of gene variants, as well as encourages preventive measures and regulatory
molecules, and cellular processes that modulate complex actions taken by governmental bodies.
traits such as behavior and disease susceptibility. This The PFC is known to undergo significant developmental
technique will enable scientists to analyze gene expression changes before individuals reach their 20s, impacting
across various specific brain regions and tissues, explore decision-making ability within this population.
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/itps.1472