Page 69 - ITPS-7-2
P. 69
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Youth brain health check and dysregulation
a high risk for any addictive behavior (hypodopaminergia), Alarmingly, the largest inequities exist across nations, with
especially drug-seeking (95%) and alcohol-seeking (64%) 80% of people affected by mental disorders living in low- and
based on GARS testing of 24 Caucasians, ages 12–19 (derived middle-income countries, which benefit from scarcely 10%
from families with RDS). These results, although from a small of global mental health resources. Unfortunately, poor rural
cohort, should encourage further extensive studies in this area. areas in the US experience a significantly higher rate of mental
disorders, including RDS behaviors such as SUD. Furthermore,
Mental disorders are widespread globally, influencing due to low income and high juvenile delinquency in rural
every community and age group, and contribute substantially communities, possibly linked to cognitive inabilities such as
to the overall disease burden, with major economic and social poor decision-making, the recommendation of a standard
consequences as well as effects on human health and rights. BHC seems prudent. While globally accepted diagnostic
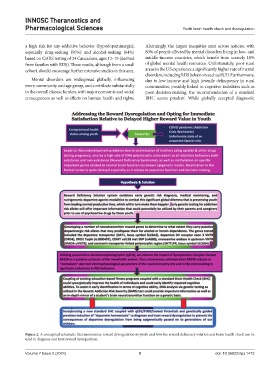
Figure 2. A conceptual schematic that summarizes reward dysregulation in youth and how the reward deficiency solution and brain health check can be
used to diagnose and treat reward dysregulation.
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2024) 9 doi: 10.36922/itps.1472