Page 46 - ITPS-7-3
P. 46
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Medicinal plants: Natural diabetes remedies
exhibit physiological effects on people. These metabolites
43
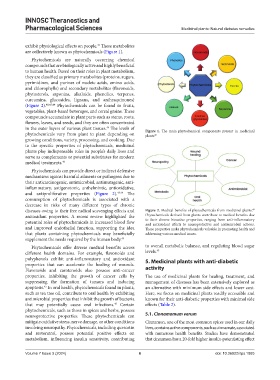
are collectively known as phytochemicals (Figure 1).
Phytochemicals are naturally occurring chemical
compounds that are biologically active and highly beneficial
to human health. Based on their roles in plant metabolism,
they are classified as primary metabolites (proteins, sugars,
pyrimidines, and purines of nucleic acids, amino acids,
and chlorophylls) and secondary metabolites (flavonoids,
phytosterols, saponins, alkaloids, phenolics, terpenes,
curcumins, glucosides, lignans, and anthraquinones)
(Figure 2). 40,43,44 Phytochemicals can be found in fruits,
vegetables, plant-based beverages, and cereal grains. These
compounds accumulate in plant parts such as stems, roots,
flowers, leaves, and seeds, and they are often concentrated
in the outer layers of various plant tissues. The levels of Figure 1. The main phytochemical components present in medicinal
44
phytochemicals vary from plant to plant depending on plants 43
growing conditions, variety, processing, and cooking. Due
to the specific properties of phytochemicals, medicinal
plants play indispensable roles in people’s daily lives and
serve as complements or potential substitutes for modern
medical treatments. 40
Phytochemicals can provide direct or indirect defensive
mechanisms against harmful ailments or pathogens due to
their anticarcinogenic, antimicrobial, antimutagenic, anti-
inflammatory, antigenotoxic, anthelmintic, antioxidative,
and antiproliferative properties (Figure 2). 43,44 The
consumption of phytochemicals is associated with a
decrease in risks of many different types of chronic
diseases owing to their free radical scavenging effects and Figure 2. Medical benefits of phytochemicals from medicinal plants.
43
antioxidant properties. A recent review highlighted the Phytochemicals derived from plants contribute to medical benefits due
potential roles of phytochemicals in increased blood flow to their diverse bioactive properties, ranging from anti-inflammatory
and antioxidant effects to neuroprotective and antimicrobial actions.
and improved endothelial function, supporting the idea These properties make phytochemicals valuable in promoting health and
that plants containing phytochemicals may beneficially addressing various medical issues.
supplement the needs required by the human body. 44
Phytochemicals offer diverse medical benefits across to overall metabolic balance, and regulating blood sugar
different health domains. For example, flavonoids and levels. 45
polyphenols exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidant 5. Medicinal plants with anti-diabetic
properties that can accelerate the healing of wounds.
Flavonoids and carotenoids also possess anti-cancer activity
properties, inhibiting the growth of cancer cells by The use of medicinal plants for healing, treatment, and
suppressing the formation of tumors and inducing management of diseases has been extensively explored as
apoptosis. In oral health, phytochemicals found in plants, an alternative with minimum side effects and lower cost.
45
such as tea tree oil, contribute to oral health by exhibiting Here, we focus on medicinal plants readily accessible and
antimicrobial properties that inhibit the growth of bacteria known for their anti-diabetic properties with minimal side
that may potentially cause oral infections. Certain effects (Table 2).
46
phytochemicals, such as those in spices and herbs, possess
neuroprotective properties. These phytochemicals can 5.1. Cinnamomum verum
mitigate oxidative stress, nerve damage, or other conditions Cinnamon, one of the most common spices used in our daily
involving neuropathy. Phytochemicals, including quercetin lives, contains active components, such as cinnamate, associated
and resveratrol, possess potential positive effects on with numerous health benefits. Studies have demonstrated
metabolism, influencing insulin sensitivity, contributing that cinnamon has a 20-fold higher insulin-potentiating effect
Volume 7 Issue 3 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/itps.1885