Page 76 - ITPS-7-3
P. 76
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Enhancers and SEs in cancer treatment
A B
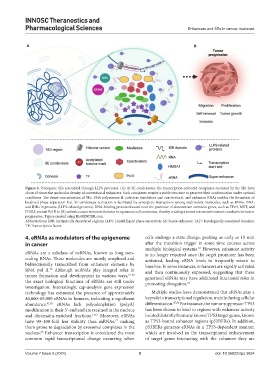
Figure 2. Oncogenic SEs assembled through LLPS processes. (A) At SE condensates, the transcription-activated complexes recruited by the SEs have
about 10 times the molecular density of conventional enhancers. Such complexes require a stable structure to preserve their conformation under optimal
conditions. The dense concentration of TFs, RNA polymerase II, cofactors (mediators and coactivators), and enhancer RNAs enables the formation of
localized phase separation foci. SE condensate activation is facilitated by synergistic interactions among multivalent molecules, such as RNAs, DNA,
and IDRs in proteins (LLPS-related proteins). RNA-binding proteins located near the promoter of downstream stemness genes, such as TP63, MET, and
FOSL1, recruit Pol II to (B) activate cancer stemness features in squamous cell carcinoma, thereby creating a tumor microenvironment conducive to tumor
progression. Figure created using BioRENDER.com.
Abbreviations: IDR: Intrinsically disordered regions; LLPS: Liquid-liquid phase separation; SE: Super-enhancer; TAD: Topologically associated domains;
TF: Transcription factor.
4. eRNAs as modulators of the epigenome cells undergo a state change, peaking as early as 15 min
in cancer after the transition trigger in some time courses across
multiple biological systems. However, enhancer activity
62
eRNAs are a subclass of ncRNAs, known as long non- is no longer required once the target promoter has been
coding RNAs. These molecules are mostly unspliced and activated, leading eRNA levels to frequently return to
bidirectionally transcribed from enhancer elements by baseline. In some instances, enhancers are rapidly activated
RNA pol II. Although ncRNAs play integral roles in and then continuously expressed, suggesting that these
56
tumor formation and development in various ways, 57-60 generated eRNAs may have additional functional roles in
the exact biological functions of eRNAs are still under promoting elongation. 64
investigation. Interestingly, cap-analysis gene expression
technology has estimated the presence of approximately Multiple studies have demonstrated that eRNAs play a
40,000–65,000 eRNAs in humans, indicating a significant key role in transcriptional regulation, mainly during cellular
abundance. 61,62 eRNAs lack polyadenylation (polyA) differentiation. 65,66 For instance, the tumor suppressor TP53
modification at their 3’-end and are retained in the nucleus has been shown to bind to regions with enhancer activity
and chromatin-enriched fractions. 17,61 Moreover, eRNAs located distantly from any known TP53 target genes, known
have 90–100-fold less stability than mRNAs, making as TP53-bound enhancer regions (p53BERs). In addition,
17
them prone to degradation by exosomal complexes in the p53BERs generate eRNAs in a TP53-dependent manner,
nucleus. Enhancer transcription is considered the most which are involved in the transcriptional enhancement
63
common rapid transcriptional change occurring when of target genes interacting with the enhancer they are
Volume 7 Issue 3 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/itps.3654