Page 16 - ITPS-7-4
P. 16
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Neurobiology of gaming disorder
of diseases were guided by epidemiologic, clinical, and purpose of Internet use has been explicitly identified as
neurobiological studies, which reflect growing scientific gaming. In such cases, the term “GD,” instead of the term
evidence about the similarities of GD with substance- “Internet addiction,” is used to describe research results
related and other addictive disorders. Initially, GD was on Internet addiction. In addition, this review excludes
5,6
considered a subtype of Internet addiction, but a review of studies focusing on GD with comorbid conditions. Table 1
the scientific literature on gaming revealed that excessive provides brief explanations for the technical terms related
gaming tends to be distinct and more likely to lead to to brain imaging techniques.
serious consequences independently. Furthermore,
7-9
since the Internet is merely a medium for accessing 2. Changes of brain reward circuit
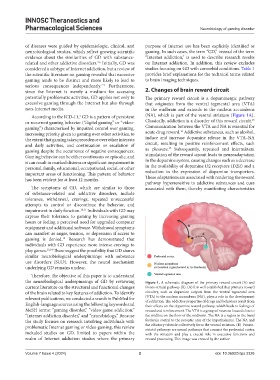
potentially problematic activities, GD applies not only to The primary reward circuit is a dopaminergic pathway
excessive gaming through the Internet but also through that originates from the ventral tegmental area (VTA)
non-Internet media. in the midbrain and extends to the nucleus accumbens
According to the ICD-11, GD is a pattern of persistent (NA), which is part of the ventral striatum (Figure 1A).
4
15
or recurrent gaming behavior (“digital gaming” or “video- Classically, addiction is a disorder of this reward circuit.
gaming”) characterized by impaired control over gaming, Communication between the VTA and NA is essential for
16
increasing priority given to gaming over other activities, to acute drug reward. Addictive substances, such as alcohol,
the extent that gaming takes precedence over other interests induce and increase dopamine release in the VTA–NA
and daily activities, and continuation or escalation of circuit, resulting in positive reinforcement effects, such
15
gaming despite the occurrence of negative consequences. as pleasure. Subsequently, repeated and intermittent
Gaming behavior can be either continuous or episodic, and stimulation of the reward circuit leads to neuroadaptation
it can result in marked distress or significant impairment in in the dopamine system, causing changes such as a decrease
personal, family, educational, occupational, social, or other in the availability of dopamine D2 receptors (D2R) and a
important areas of functioning. This pattern of behavior reduction in the expression of dopamine transporters.
has been evident for at least 12 months. These adaptations are associated with rendering the reward
pathway hypersensitive to addictive substances and cues
The symptoms of GD, which are similar to those associated with them, thereby manifesting characteristics
of substance-related and addictive disorders, include
tolerance, withdrawal, cravings, repeated unsuccessful
attempts to control or discontinue the behavior, and
impairment in daily function. 10,11 Individuals with GD may
express their tolerance to gaming by increasing gaming
hours or feeling a perceived need for upgraded computer
equipment and additional software. Withdrawal symptoms
can manifest as anger, tension, or depression if access to
12
gaming is denied. Research has demonstrated that
individuals with GD experience more intense cravings to
play games. 13,14 These suggest the possibility that GD shares
similar neurobiological underpinnings with substance
use disorders (SUD). However, the neural mechanism
underlying GD remains unclear.
Therefore, the objective of this paper is to understand
the neurobiological underpinnings of GD by reviewing Figure 1. A schematic diagram of the primary reward circuit (A) and
current literature on the structural and functional changes fronto-striatal pathway (B). (A) It is well established that primary reward
of the brain related to key features of addiction. To identify circuitry, such as dopamine outputs from the ventral tegmental area
relevant publications, we conducted a search in PubMed for (VTA) to the nucleus accumbens (NA), plays a role in the development
of addiction. The addictive properties of drugs and behaviors result from
English-language sources using the following keywords and their effects on the dopamine reward pathway, which leads to feelings of
MeSH terms: “gaming disorder,” “video game addiction,” reward and reinforcement. The VTA is a group of neurons located close to
“Internet addiction disorder,” and “neurobiology.” Because the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The NA is a region in the basal
the study focuses on research involving individuals with forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. The NA and
problematic Internet gaming or video gaming, this review the olfactory tubercle collectively form the ventral striatum. (B) Fronto-
striatal pathways are neural pathways that connect the prefrontal cortex
included studies on GD, limited to papers within the with the striatum and play a crucial role in executive functions and
realm of Internet addiction studies where the primary reward processing. This image was created by the author.
Volume 7 Issue 4 (2024) 2 doi: 10.36922/itps.3326