Page 39 - ITPS-8-1
P. 39
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Ketamine for cocaine use disorder
by an inability to control drug seeking and intake despite considered mature. 14,15 During cocaine withdrawal, these
damaging consequences. The addictive property of synapses mature quickly by recruiting AMPARs, leading
3
cocaine is associated with its ability to interact with the to depolarization, NMDAR opening, calcium ion release,
mesolimbic pathway (Figure 1). This pathway includes and eventually long-term potentiation, thus promoting
the ventral tegmental area (VTA) innervating the ventral addiction. 12
striatum, which includes nucleus accumbens (NAc), an Despite decades of research, most treatments for CUD
area important for forming and maintaining addiction- rely on psychosocial interventions as there are currently
related memory and contributes to relapse. Most NAc no Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved
4
neurons are medium spiny neurons (MSN), which are pharmacological treatments. However, ketamine, a non-
1
γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic neurons classified by competitive NMDAR antagonist, has gained attention
the type of dopamine receptors they express. Although as a promising pharmacological treatment for CUD.
signaling pathways of these two types of neurons are highly Ketamine is a racemic mixture of two enantiomers, S and
complex, MSNs that express type 1 dopamine receptors R ketamine, with the S enantiomer (esketamine) being
5-7
(D1-MSN) are classically associated with rewards. MSNs more potent. While ketamine has been used as a general
that express type 2 dopamine receptors (D2-MSN) can lead anesthetic due to its dissociative effects, a subanesthetic
to decreased motivation and locomotion (Figure 1). dose of esketamine has been approved to treat depression
8,9
16
Cocaine interacts with the mesolimbic pathway by Although ketamine has a history of misuse as a recreational
remodeling glutamatergic synapses, especially those in drug, 17,18 no overdose or fatality has been reported when
D1-MSN, 10-12 creating “silent synapses,” which are immature it is used in a therapeutic setting. 18,19 Recently, due to
glutamatergic synapses that contain N-methyl-D-aspartate ketamine’s antagonistic effect and the association between
receptors (NMDAR) but not α-amino-3-hydroxy-5- depression and substance use disorders, there has been
methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPAR). a lot of interest in exploring its therapeutic potential in
13
NMDAR is a glutamate-gated calcium channel that treating various types of addictions. 20
activates when AMPAR-induced depolarization displaces In this narrative review, we summarize the evidence
a magnesium ion blocking it (Figure 2). Lacking AMPARs, presented in both pre-clinical and clinical studies
these “silent synapses” cannot be activated and thus are not illustrating ketamine’s effect in reducing cue-induced
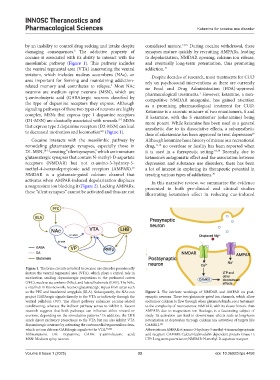
Figure 1. The brain circuits involved in cocaine use disorder prominently
feature the ventral tegmental area (VTA), which plays a critical role in
motivation, sending dopaminergic projections to the prefrontal cortex
(PFC), nucleus accumbens (NAc), and lateral habenula (LHB). The NAc,
a vital hub in this network, receives glutamatergic inputs from areas such
as the PFC and basolateral amygdala (BLA). Subsequently, the NAc can Figure 2. The intricate workings of NMDAR and AMPAR on post-
project GABAergic signals directly to the VTA or indirectly through the synaptic neurons. These two glutamate-gated ion channels, which allow
ventral pallidum (VP). The direct pathway enhances cocaine-related sodium or calcium to flow through when glutamate binds, are a testament
conditioning, whereas the indirect pathway serves to inhibit it. Recent to the complexity of neuroscience. NMDAR, with its slower kinetic than
research suggests that both pathways can influence either reward or AMPAR’s due to magnesium ion blockage, is a fascinating subject of
aversion, depending on the stimulation patterns. In addition, the LHB study. Its activation can lead to downstream effects such as long-term
6
sends direct excitatory projections to the VTA but can also inhibit VTA potentiation or depression through calcium ion activation of targets like
dopaminergic neurons by activating the rostromedial tegmental nucleus, CAMKII. 123
which in turn delivers GABAergic signals to the VTA. 64,122 Abbreviations: AMPAR: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic
Abbreviations: DA: Dopamine; GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid; acid receptor; CAMKII: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II;
MSN: Medium spiny neuron. LTP: Long-term potentiation; NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor.
Volume 8 Issue 1 (2025) 33 doi: 10.36922/itps.4458