Page 115 - ITPS-8-3
P. 115
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Cholesteatoma enrichment pathways for drug repurposing
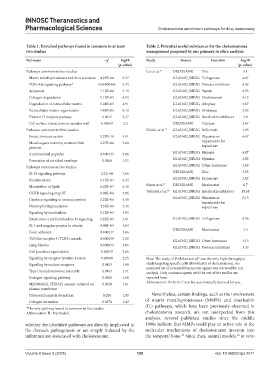
Table 1. Enriched pathways found in common in at least Table 2. Potential useful substances for the cholesteatoma
two studies management proposed by our primary in silico analysis
Pathways −χ 2 log10 Study Source Function ‑log10
(p‑value) (p‑value)
Pathways common in four studies Lee et al. 12 DRUGBANK Zinc 5.1
Matrix metalloproteinases and their activation 4.25E–06 5.37 GLAD4U_DRUG Collagenase 4.87
PI3K-Akt signaling pathway* 0.00000446 5.35 GLAD4U_DRUG Protease inhibitors 4.55
Apoptosis 7.12E–06 5.15 GLAD4U_DRUG Papain 4.53
Collagen degradation 1.12E–05 4.95 GLAD4U_DRUG Ustekinumab 4.12
Degradation of extracellular matrix 1.24E–05 4.91 GLAD4U_DRUG Alteplase 3.87
Extracellular matrix organization 7.48E–05 4.13 GLAD4U_DRUG Urokinase 3.83
Vitamin D receptor pathway 0.0017 2.77 GLAD4U_DRUG Interleukin inhibitors 3.8
Cell surface interactions at vascular wall 0.00629 2.2 DRUGBANK Calcium 3.67
Pathways common in three studies Klenke et al. 13 GLAD4U_DRUG Infliximab 4.95
Innate immune system 1.23E–10 9.91 GLAD4U_DRUG Heparins or 4.87
Metal sequestration by antimicrobial 2.27E–06 5.64 heparinoids for
proteins topical use
Antimicrobial peptides 0.000133 3.88 GLAD4U_DRUG Heparin 4.87
Formation of cornified envelope 0.0268 1.57 GLAD4U_DRUG Nystatin 3.92
Pathways common in two studies GLAD4U_DRUG Other hormones 3.89
IL-18 signaling pathway 2.2E–08 7.66 DRUGBANK Zinc 3.85
Keratinization 5.71E–07 6.24 GLAD4U_DRUG Etanercept 3.82
Metabolism of lipids 6.62E–07 6.18 Kwon et al. 15 DRUGBANK Marimastat 6.7
CCKR signaling map ST 1.09E–06 5.96 Tokuriki et al. 10 GLAD4U_DRUG Interleukin inhibitors 15.65
Cytokine signaling in immune system 3.22E–06 5.49 GLAD4U_DRUG Heparins or 5.13
heparinoids for
Neutrophil degranulation 4.33E–06 5.36 topical use
Signaling by interleukins 1.12E–05 4.95
Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 signaling 1.23E–05 4.91 GLAD4U_DRUG Collagenase 4.56
IL-1 and megakaryocytes in obesity 9.09E–05 4.04
DRUGBANK Marimastat 3.4
Focal adhesion 0.000217 3.66
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) cascade 0.000559 3.25 GLAD4U_DRUG Other hormones 3.13
Lung fibrosis 0.000873 3.06
GLAD4U_DRUG Protease inhibitors 3.43
Cell junction organization 0.00219 2.66
Signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases 0.00568 2.25 Note: The study of Yoshikawa et al. was the only high-throughput
8
Signaling by nuclear receptors 0.0103 1.99 study targeting specific cells (fibroblasts) of cholesteatoma. An
extensive list of potential therapeutic agents was retrieved by our
Type I hemidesmosome assembly 0.0193 1.71 analysis. Only common agents with the rest of the studies are
Estrogen signaling pathway 0.0209 1.68 reported here.
MyD88:MAL (TIRAP) cascade initiated on 0.0248 1.61 Abbreviation: GLADU: Gene list automatically derived for you.
plasma membrane
Fibronectin matrix formation 0.028 1.55 Nevertheless, certain findings, such as the involvement
Collagen formation 0.0374 1.43 of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and interleukin
*The only pathway found in common in five studies. (IL) pathways, which have been previously observed in
Abbreviation: IL: Interleukin. cholesteatoma research, are not unexpected from this
analysis. Several published studies since the middle
whether the identified pathways are directly implicated in 1990s indicate that MMPs could play an active role in the
the disease’s pathogenesis or are simply induced by the molecular mechanisms of cholesteatoma invasion into
inflammation associated with cholesteatoma. the temporal bone. Since then, animal models, in vitro
18
17
Volume 8 Issue 3 (2025) 109 doi: 10.36922/itps.2571