Page 75 - JCAU-5-3
P. 75
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Spatial scale plasticity of urban residential areas
A B C
Figure 5. Distribution of the number of days with cases in different residential areas. (A) In residential quarters. (B) In commercial housing. (C) In workers’
new villages. Source: Drawings by the authors
A B C
Figure 6. Relationship between the feature of residential quarters and the number of days with new cases. (A) The average number of floors. (B) The floor
area ratio (FAR; total floor area/total area of the plot). (C) The residential quarter scale. Source: Graphs by the authors
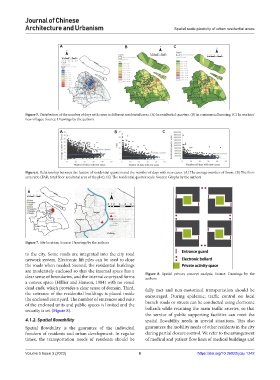
Figure 7. Site location. Source: Drawings by the authors
to the city. Some roads are integrated into the city road
network system. Electronic lift piles can be used to close
the roads when needed. Second, the residential buildings
are moderately enclosed so that the internal space has a Figure 8. Spatial privacy concept analysis. Source: Drawings by the
clear sense of boundaries, and the internal courtyard forms authors
a convex space (Hillier and Hanson, 1984) with no visual
dead ends, which provides a clear sense of domain. Third, fully met and non-motorized transportation should be
the entrance of the residential buildings is placed inside encouraged. During epidemic, traffic control on local
the enclosed courtyard. The number of entrances and exits
of the enclosed units and public spaces is limited and the branch roads or streets can be conducted using electronic
security is set (Figure 8). bollards while retaining the main traffic arteries, so that
the service of public supporting facilities can meet the
4.1.2. Spatial flowability spatial flowability needs in special situations. This also
Spatial flowability is the guarantee of the individual guarantees the mobility needs of other residents in the city
freedom of residents and urban development. In regular during partial closure control. We refer to the arrangement
times, the transportation needs of residents should be of medical and patient flow lines of medical buildings and
Volume 5 Issue 3 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.1242