Page 21 - JCAU-5-4
P. 21
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Spatial morphology of cohesive village
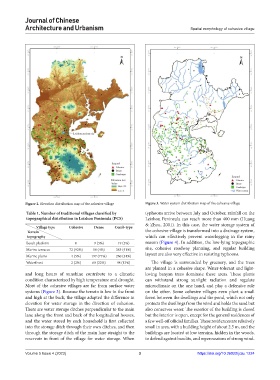
Figure 2. Elevation distribution map of the cohesive village Figure 3. Water system distribution map of the cohesive village
Table 1. Number of traditional villages classified by typhoons arrive between July and October, rainfall on the
topographical distribution in Leizhou Peninsula (PCS) Leizhou Peninsula can reach more than 400 mm (Huang
& Zhou, 2001). In this case, the water storage system of
Village type Cohesive Dense Comb‑type
Terrain the cohesive village is transformed into a drainage system,
topography which can effectively prevent waterlogging in the rainy
Basalt platform 0 9 (3%) 19 (2%) season (Figure 4). In addition, the low-lying topographic
Marine terraces 72 (92%) 10 (4%) 385 (51%) site, cohesive roadway planning, and regular building
Marine plains 4 (5%) 197 (71%) 260 (34%) layout are also very effective in resisting typhoons.
Waterfront 2 (2%) 60 (22%) 98 (13%) The village is surrounded by greenery, and the trees
are planted in a cohesive shape. Water-tolerant and light-
and long hours of sunshine contribute to a climatic loving banyan trees dominate these areas. These plants
condition characterized by high temperature and drought. can withstand strong sunlight radiation and regulate
Most of the cohesive villages are far from surface water microclimate on the one hand, and play a defensive role
systems (Figure 3). Because the terrain is low in the front on the other. Some cohesive villages even plant a small
and high at the back, the village adapted the difference in forest between the dwellings and the pond, which not only
elevation for water storage in the direction of cohesion. protects the dwellings from the wind and holds the sand but
There are water storage ditches perpendicular to the main also conserves water. The exterior of the building is closed
lane along the front and back of the longitudinal houses, but the interior is open, except for the general residences of
and the water stored by each household is first collected a few well-off official families. These residences are relatively
into the storage ditch through their own ditches, and then small in area, with a building height of about 2.5 m, and the
through the storage ditch of the main lane straight to the buildings are located at low terrains, hidden in the woods,
reservoir in front of the village for water storage. When to defend against bandits, and repercussions of strong wind.
Volume 5 Issue 4 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.1224