Page 37 - JCAU-6-1
P. 37
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Perception of pedestrian environment
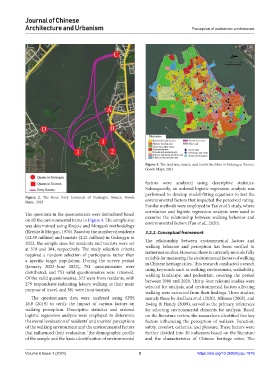
Figure 3. The land use, routes, and tourist facilities in Gulangyu. Source:
Gaode Maps, 2023
factors were analyzed using descriptive statistics.
Subsequently, an ordered logistic regression analysis was
performed to develop model-fitting equations to test the
Figure 2. The three ferry terminals of Gulangyu. Source: Gaode environmental factors that impacted the perceived rating.
Maps, 2023
Similar methods were employed in Tan et al.’s study, where
correlation and logistic regression analysis were used to
The questions in the questionnaire were formulated based examine the relationship between walking behavior and
on all the environmental items in Figure 4. The sample size environmental factors (Tan et al., 2020).
was determined using Krejcie and Morgan’s methodology
(Krejcie & Morgan, 1970). Based on the number of residents 3.2.2. Conceptual framework
(12.59 million) and tourists (2.21 million) in Gulangyu in
2022, the sample sizes for residents and tourists were set The relationship between environmental factors and
at 370 and 384, respectively. The study selection criteria walking behavior and perception has been verified in
numerous studies. However, there is currently no scale fully
required a random selection of participants rather than
a specific target population. During the survey period suitable for measuring the environmental factors of walking
(January 2022–June 2022), 781 questionnaires were in Chinese heritage cities. This research conducted a search
using keywords such as walking environment, walkability,
distributed, and 753 valid questionnaires were returned. walking landscape, and pedestrian, covering the period
Of the valid questionnaires, 372 were from residents, with between 2000 and 2020. Thirty-four relevant studies were
279 respondents indicating leisure walking as their main selected for analysis, and environmental factors affecting
purpose of travel, and 381 were from tourists.
walking were extracted from their findings. Three studies,
The questionnaire data were analyzed using SPSS namely those by Arellana et al. (2020), Alfonzo (2005), and
26.0 (2019) to verify the impact of various factors on Ewing & Handy (2009), served as the primary references
walking perception. Descriptive statistics and ordered for selecting environmental elements for analysis. Based
logistic regression analysis were employed to determine on the literature review, the researchers identified five key
the overall evaluation of residents’ and tourists’ perceptions factors influencing the perception of walkers: Function,
of the walking environment and the environmental factors safety, comfort, esthetics, and pleasure. These factors were
that influenced their evaluation. The demographic profile further divided into 30 indicators based on the literature
of the sample and the basic identification of environmental and the characteristics of Chinese heritage cities. The
Volume 6 Issue 1 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.1879