Page 16 - JCBP-2-3
P. 16
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics The antidepressant effect of ketamine
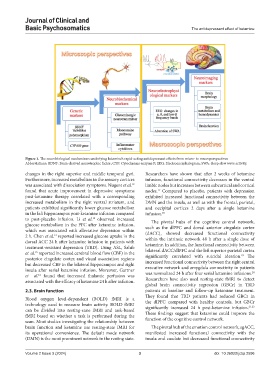
Figure 1. The neurobiological mechanisms underlying ketamine’s rapid-acting antidepressant effects from micro- to macroperspectives
Abbreviations: BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CYP: Cytochrome enzyme P; EEG: Electroencephalogram; SWA: Sleep slow wave activity.
changes in the right superior and middle temporal gyri. Researchers have shown that after 2 weeks of ketamine
Furthermore, increased metabolism in the sensory cortices infusion, functional connectivity decreases in the ventral
was associated with dissociation symptoms. Nugent et al. limbic nodes but increases between subcortical and cortical
12
found that acute improvement in depressive symptoms nodes. Compared to placebo, patients with depression
17
post-ketamine therapy correlated with a corresponding exhibited increased functional connectivity between the
increased metabolism in the right ventral striatum, and DMN and the insula, as well as with the frontal, parietal,
patients exhibited significantly lower glucose metabolism and occipital cortices 2 days after a single ketamine
in the left hippocampus post-ketamine infusion compared infusion. 18
to post-placebo infusion. Li et al. observed increased The pivotal hubs of the cognitive control network,
13
glucose metabolism in the PFC after ketamine infusion, such as the dlPFC and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex
which was associated with alleviative depression within (dACC), showed decreased functional connectivity
2 h. Chen et al. reported increased glucose uptake in the within the intrinsic network 48 h after a single dose of
14
dorsal ACC 24 h after ketamine infusion in patients with ketamine. In addition, the functional connectivity between
treatment-resistant depression (TRD). Using ASL, Sahib
et al. reported increased cerebral blood flow (CBF) in the bilateral dACC/dlPFC and the left superior parietal cortex
15
19
posterior cingulate cortex and visual association regions significantly correlated with suicidal ideation. The
but decreased CBF in the bilateral hippocampus and right increased functional connectivity between the right central
insula after serial ketamine infusion. Moreover, Gartner executive network and amygdala connectivity in patients
20
et al. found that increased thalamic perfusion was was normalized 24 h after four serial ketamine infusions.
16
associated with the efficacy of ketamine 24 h after infusion. Researchers have also used resting-state fMRI to detect
global brain connectivity regression (GBCr) in TRD
2.3. Brain function patients at baseline and follow-up ketamine treatment.
They found that TRD patients had reduced GBCr in
Blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) fMRI is a the dlPFC compared with healthy controls, but GBCr
technology used to measure brain activity. BOLD fMRI significantly increased 24 h post-ketamine infusion. 21,22
can be divided into resting-state fMRI and task-based These findings suggest that ketamine could improve the
fMRI based on whether a task is performed during the function of the cognitive control network.
scan. Most studies investigating the relationship between
brain function and ketamine use resting-state fMRI for The pivotal hub of the emotion control network, sgACC,
its operational convenience. The default mode network manifested increased functional connectivity with the
(DMN) is the most prominent network in the resting state. insula and caudate but decreased functional connectivity
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.2596