Page 37 - JCBP-2-4
P. 37
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Core depressive symptoms of peripartum women
A B C D
E F G H
I J
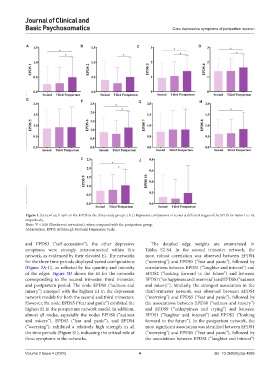
Figure 1. Score of each item on the EPDS in the three study groups. (A-J) Represent comparison of scores at different stages of the EPDS for items 1 to 10,
respectively.
Note: *P < 0.05 (Bonferroni correction), when compared with the postpartum group.
Abbreviation: EPDS: Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale.
and EPDS3 (“self-accusation”), the other depressive The detailed edge weights are enumerated in
symptoms were strongly interconnected within this Tables S2-S4. In the second trimester network, the
network, as evidenced by their elevated EI. The networks most robust correlation was observed between EPDS4
for the three time periods displayed varied configurations (“worrying”) and EPDS5 (“fear and panic”), followed by
(Figure 3A-C), as reflected by the quantity and intensity correlations between EPDS1 (“laughter and interest”) and
of the edges. Figure 3D shows the EI for the networks EPDS2 (“looking forward to the future”) and between
corresponding to the second trimester, third trimester, EPDS7 (“unhappiness and insomnia”) and EPDS8 (“sadness
and postpartum period. The node EPDS8 (“sadness and and misery”). Similarly, the strongest association in the
misery”) emerged with the highest EI in the depression third-trimester network was observed between EPDS4
network models for both the second and third trimesters. (“worrying”) and EPDS5 (“fear and panic”), followed by
However, the node EPDS5 (“fear and panic”) exhibited the the associations between EPDS8 (“sadness and misery”)
highest EI in the postpartum network model. In addition, and EPDS9 (“unhappiness and crying”) and between
almost all nodes, especially the nodes EPDS8 (“sadness EPDS1 (“laughter and interest”) and EPDS2 (“looking
and misery”), EPDS5 (“fear and panic”), and EPDS4 forward to the future”). In the postpartum network, the
(“worrying”), exhibited a relatively high strength in all most significant association was identified between EPDS4
the time periods (Figure S1), indicating the critical role of (“worrying”) and EPDS5 (“fear and panic”), followed by
these symptoms in the networks. the associations between EPDS1 (“laughter and interest”)
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.4089