Page 61 - JCBP-2-4
P. 61
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Schizophrenia and metabolism
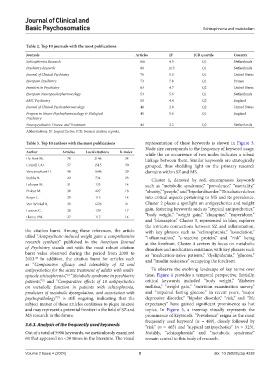
Table 2. Top 10 journals with the most publications
Journals Articles IF JCR quartile Country
Schizophrenia Research 166 4.5 Q1 Netherlands
Psychiatry Research 80 11.3 Q1 Netherlands
Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 76 5.3 Q1 United States
European Psychiatry 73 7.8 Q1 France
Frontiers in Psychiatry 63 4.7 Q2 United States
European Neuropsychopharmacology 53 5.6 Q1 Netherlands
BMC Psychiatry 50 4.4 Q2 England
Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 48 2.9 Q2 United States
Progress in Neuro‑Psychopharmacology & Biological 45 5.6 Q1 England
Psychiatry
Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment 44 3.2 Q2 Netherlands
Abbreviations: IF: Impact factor; JCR: Journal citation reports.
Table 3. Top 10 authors with the most publications representation of these keywords is shown in Figure 3.
Node size corresponds to the frequency of keyword usage,
Author Articles Local citations h‑index
while the co-occurrence of two nodes indicates a robust
De Hert M. 70 2146 34 linkage between them. Similar keywords are strategically
Correll C.U. 57 1515 30 grouped, thus shedding light on the primary research
Vancampfcort D. 48 1646 29 domains within SZ and MS.
Stubbs B. 42 734 23 Cluster 1, denoted by red, encompasses keywords
Leboyer M. 31 135 14 such as “metabolic syndrome,” “prevalence,” “mortality,”
Probst M. 30 427 18 “obesity,” “people,” and “bipolar disorder.” This cluster delves
Boyer L. 29 115 14 into critical aspects pertaining to MS and its prevalence.
Van Winkel R. 29 1276 21 Cluster 2 places a spotlight on antipsychotics and weight
Lancon C. 28 129 17 gain, featuring keywords such as “atypical antipsychotics,”
“body weight,” “weight gain,” “clozapine,” “risperidone,”
Llorca P.M. 27 117 14
and “olanzapine.” Cluster 3, represented in blue, explores
the intricate connections between SZ and inflammation,
the citation burst. Among these references, the article with key phrases such as “schizophrenia,” “association,”
titled “Antipsychotic‑induced weight gain: a comprehensive “inflammation,” “c-reactive protein,” and “risk” being
research synthesis” published in the American Journal at the forefront. Cluster 4 centers its focus on metabolic
of Psychiatry stands out with the most robust citation disorders and medication resistance, with key phrases such
burst value observed during the period from 2008 to as “medication-naive patients,” “dyslipidemia,” “glucose,”
2013. In addition, the citation burst for articles such and “insulin resistance” occupying the forefront.
20
as “Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 32 oral
antipsychotics for the acute treatment of adults with multi‑ To observe the evolving landscape of key terms over
episode schizophrenia,” “Metabolic syndrome in psychiatric time, Figure 4 provides a temporal perspective. Initially,
21
patients,” and “Comparative effects of 18 antipsychotics critical keywords included “body weight,” “diabetes
22
on metabolic function in patients with schizophrenia, mellitus,” “weight gain,” “nutrition examination survey,”
predictors of metabolic dysregulation, and association with and “impaired fasting glucose.” In recent years, “major
psychopathology” is still ongoing, indicating that the depressive disorder,” “bipolar disorder,” “risk,” and “life
23
subject matter of these articles continues to pique interest expectancy” have gained significant prominence as hot
and may represent a potential frontier in the field of SZ and topics. In Figure 5, a treemap visually represents the
MS research in the future. prominence of keywords. “Prevalence” reigns as the most
frequently used keyword (n = 489), closely followed by
3.6.3. Analysis of the frequently used keywords “risk” (n = 465) and “atypical antipsychotics” (n = 323).
Out of a total of 5906 keywords, we meticulously examined Notably, “schizophrenia” and “metabolic syndrome”
60 that appeared no <30 times in the literature. The visual remain central to this body of research.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.4238