Page 74 - JCBP-2-4
P. 74
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Profiles of attention and executive function in epilepsy versus psychogenic seizures
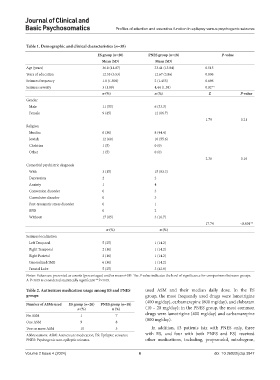
Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics (n=38)
ES group (n=20) PNES group (n=18) P‑value
Mean (SD) Mean (SD)
Age (years) 36.8 (14.07) 33.41 (13.04) 0.515
Years of education 12.55 (3.53) 12.67 (3.86) 0.806
Seizures frequency 1.8 (1.508) 2 (1.455) 0.696
Seizures severity 3 (1.89) 4.44 (1.58) 0.02**
n (%) n (%) Z P‑value
Gender
Male 11 (55) 6 (33.3)
Female 9 (45) 12 (66.7)
1.79 0.21
Religion
Muslim 6 (30) 8 (44.4)
Jewish 12 (60) 10 (55.6)
Christian 1 (5) 0 (0)
Other 1 (5) 0 (0)
2.36 0.16
Comorbid psychiatric diagnosis
With 3 (15) 15 (83.3)
Depression 2 2
Anxiety 1 4
Conversion disorder 0 3
Convulsive disorder 0 3
Post-traumatic stress disorder 0 1
BPD 0 2
Without 17 (85) 3 (16.7)
17.74 <0.001**
n (%) n (%)
Seizures localization
Left Temporal 5 (25) 1 (14.2)
Right Temporal 2 (10) 1 (14.2)
Right Parietal 2 (10) 1 (14.2)
Generalized/JME 6 (30) 1 (14.2)
Frontal Lobe 5 (25) 3 (42.8)
Notes: Values are presented as counts (percentages) and/or means±SD. The P-value indicates the level of significance for comparisons between groups.
A P<0.05 is considered statistically significant **P<0.05.
Table 2. Antiseizure medication usage among ES and PNES used ASM and their median daily dose. In the ES
groups group, the most frequently used drugs were lamotrigine
(400 mg/day), carbamazepine (800 mg/day), and clobazam
Number of ASMs used ES group (n=20) PNES group (n=18)
n (%) n (%) (10 – 20 mg/day); in the PNES group, the most common
No ASM 1 7 drugs were lamotrigine (400 mg/day) and carbamazepine
One ASM 9 8 (800 mg/day).
Two or more ASM 10 3 In addition, 13 patients (six with PNES only, three
Abbreviations: ASM: Antiseizure medication; ES: Epileptic seizures; with ES, and four with both PNES and ES) received
PNES: Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. other medications, including, propranolol, mirabegron,
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.3847