Page 16 - JCBP-3-1
P. 16
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Somatic symptom disorder etiology
transmission. After testing the involvement of CA3 region
hippocampal neurons in the pain perception of rats,
Li et al. noted, “there is substantial evidence indicating
that the hippocampal formation is involved in pain
processing”. 98,p.559 The authors suggest that hippocampal
mAChR involvement in pain processing enhances organism
survival because it facilitates learning and memory
about how to avoid reinjury from noxious or dangerous
situations. In a very recent study, Mueller et al. identified
82
ACh’s role in allowing the PNS to remain over-activated,
triggering inflammation. Along with nAChRs, mAChRs,
and GABAergic receptors on neurons in the hippocampus
are NMDA receptors (Figure 2). Because of interactions
99
between these four receptors, response to trauma affects
not only memory but also pain perception. 46,59,82 When
ACh binds with mAChRs, one result is that glutamate is
released. Glutamate not only binds with its own receptors
but also NMDA receptors. 100,101 NMDA receptors are the
primary activators of neuropathic SNS pain activation. 59,70,82
In the case of inescapable trauma, a hypocortisol
condition allows normal ACh activation of mAChRs,
preventing excessive glutamate release, so NMDA receptors
and the SNS are not turned “on.” Furthermore, early in any
trauma response, SIA is triggered by catecholamines that
stimulate both CRH production, and turn “on” mAChRs in
the nucleus raphe magnus of the spine. SIA in the nucleus
66
raphe magnus benefits an organism by suppressing pain but
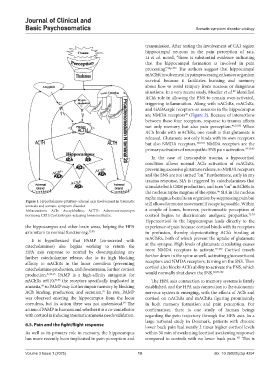
Figure 1. Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis involvement in traumatic still allows for motor movement if escape is possible. Within
amnesia and somatic symptom disorder
Abbreviations: ACh: Acetylcholine; ACTH: Adrenocorticotropin a couple of hours, however, peritraumatic perception of
hormone; CRH: Corticotropin-releasing hormone/factor. control begins to discriminate analgesic properties. 73,74
Hypercortisol in the hippocampus leads directly to the
the hippocampus and other brain areas, helping the HPA experience of pain because cortisol binds with its receptors
axis return to normal functioning. 55,83 in profusion, thereby depotentiating ACh’s binding at
It is hypothesized that PAMP (co-secreted with mAChRs, both of which prevent the uptake of glutamate
catecholamines) also begins working to return the at the synapse. High levels of glutamate circulating causes
HPA axis response to normal by downregulating any more NMDA receptors to activate. 59,100 Cortisol travels
further catecholamine release, due to its high blocking further down in the spine as well, activating glucocorticoid
affinity to nAChRs in the locus coeruleus (preventing receptors and NMDA receptors, turning on the SNS. Then
catecholamine production, and downstream, further cortisol cortisol also blocks ACh’s ability to activate the PNS, which
production. 87,94,95 PAMP is a high-affinity antagonist for would normally shut down the SNS. 82,89,102
nAChRs α9/10, 85,86 the receptors specifically implicated in The HPA axis connection to memory systems is firmly
amnesia, so PAMP may further impair memory by blocking established, and the HPA axis connection to the autonomic
96
ACh binding, production, and secretion. In rats, PAMP nervous system is emerging, with the effects of ACh and
97
was observed entering the hippocampus from the locus cortisol on nAChRs and mAChRs figuring prominently
coeruleus, but its action there was not understood. The in both memory formation and pain perception. For
94
action of PAMP in humans and whether it is a co-contributor confirmation, there is one study of human beings
with cortisol in inducing traumatic amnesia needs validation. regarding the pain trajectory through the HPA axis. In a
large national study in Denmark, patients with chronic
6.5. Pain and the fight/flight response lower back pain had nearly 2 times higher cortisol levels
As well as its primary role in memory, the hippocampus within 30 min of awakening (cortisol awakening response)
has more recently been implicated in pain perception and compared to controls with no lower back pain. This is
103
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 10 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.4254