Page 19 - JCBP-3-1
P. 19
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Somatic symptom disorder etiology
compared to normal controls, but they overvalue body elevated PAMP co-secretion, further preventing ACh binding
messages. 3 with nAChRs in the hippocampus – augmenting amnesia. In
the spinal dorsal root horn, PAMP competes with ACh to
8.2. T-A-P model bind with mAChRs and competes with endorphins to bind
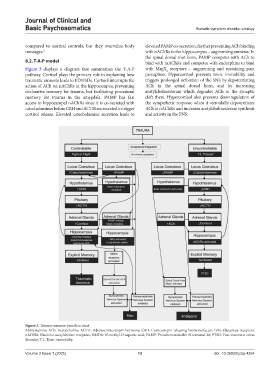
Figure 3 displays a diagram that summarizes the T-A-P with MrgX receptors – augmenting and sustaining pain
2
pathway. Cortisol plays the primary role in explaining how perception. Hypercortisol prevents tonic immobility and
traumatic amnesia leads to PD/FSDs. Cortisol interrupts the triggers prolonged activation of the SNS by depotentiating
action of ACh on nAChRs in the hippocampus, preventing ACh in the spinal dorsal horn, and by increasing
declarative memory for trauma, but facilitating procedural acetylcholinesterase which degrades ACh in the synaptic
memory for trauma in the amygdala. PAMP has fast cleft there. Hypercortisol also prevents downregulation of
access to hippocampal nAChRs since it is co-secreted with the sympathetic response when it steroidally depotentiates
catecholamines before CRH and ACTH are secreted to trigger ACh at nAChRs and increases acetylcholinesterase synthesis
cortisol release. Elevated catecholamine secretion leads to and activity in the PNS.
Figure 3. Trauma-amnesia-pain flow chart
Abbreviations: ACh: Acetylcholine; ACTH: Adrenocorticotropin hormone; CRH: Corticotropin-releasing hormone/factor; GRs: Glutamate receptors;
nAChRs: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors; NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartic acid; PAMP: Proadrenomedullin N terminal-20; PTSD: Post-traumatic stress
disorder; T.I.: Tonic immobility.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 13 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.4254