Page 7 - JCTR-10-1
P. 7
Lv et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(1): 1-8 3
A B C
D E F
G H I
J K
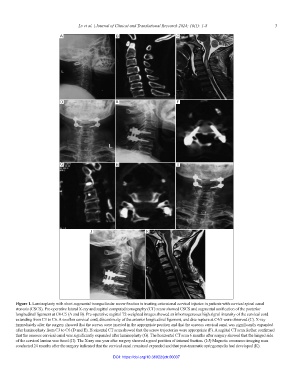
Figure 1. Laminoplasty with short-segmental transpedicular screw fixation in treating extensional cervical injuries in patients with cervical spinal canal
stenosis (CSCS). Pre-operative lateral X-ray and sagittal computed tomography (CT) scans showed CSCS and segmental ossification of the posterior
longitudinal ligament at C4-C5 (A and B). Pre-operative sagittal T2-weighted images showed an inhomogeneous high signal intensity of the cervical cord
extending from C3 to C6. A swollen cervical cord, discontinuity of the anterior longitudinal ligament, and disc rupture at C4/5 were observed (C). X-ray
immediately after the surgery showed that the screws were inserted in the appropriate position and that the osseous cervical canal was significantly expanded
after laminoplasty from C3 to C6 (D and E). Horizontal CT scan showed that the screw trajectories were appropriate (F). A sagittal CT scan further confirmed
that the osseous cervical canal was significantly expanded after laminoplasty (G). The horizontal CT scan 6 months after surgery showed that the hinged side
of the cervical lamina was fused (H). The X-ray one year after surgery showed a good position of internal fixation. (I-J) Magnetic resonance imaging scan
conducted 24 months after the surgery indicated that the cervical canal remained expanded and that post-traumatic syringomyelia had developed (K).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.00037