Page 40 - JCTR-11-2
P. 40
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research miRNA in pneumonia and pulmonary fibrosis
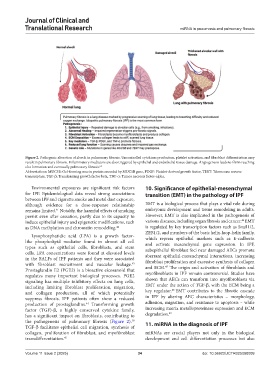
Figure 2. Pathogenic alteration of alveoli in pulmonary fibrosis. Uncontrolled cytokines production, platelet activation, and fibroblast differentiation may
result in pulmonary fibrosis. Inflammatory mediators are also triggered by epithelial and endothelial tissue damage. Angiogenesis leads to fibrin reaching
clot formation and eventually pulmonary fibrosis. 68
Abbreviations: MUC5B: Gel-forming mucin protein encoded by MUC5B gene, PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor, TERT: Telomerase reverse
transcriptase, TGF-β; Transforming growth factor beta; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
Environmental exposures are significant risk factors 10. Significance of epithelial-mesenchymal
for IPF. Epidemiological data reveal strong associations transition (EMT) in the pathology of IPF
between IPF and cigarette smoke and metal dust exposure,
although evidence for a dose-response relationship EMT is a biological process that plays a vital role during
remains limited. Notably, the harmful effects of smoking embryonic development and tissue remodeling in adults.
41
persist even after cessation, partly due to its capacity to However, EMT is also implicated in the pathogenesis of
46
induce epithelial injury and epigenetic modifications, such various diseases, including organ fibrosis and cancer. EMT
as DNA methylation and chromatin remodeling. 42 is regulated by key transcription factors such as Snail1/2,
ZEB1/2, and members of the basic helix-loop-helix family,
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a growth factor- which repress epithelial markers such as E-cadherin
like phospholipid mediator found in almost all cell and activate mesenchymal gene expression. In IPF,
types such as epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and stem subepithelial fibroblast foci near damaged AECs promote
cells. LPA concentrations were found at elevated levels aberrant epithelial-mesenchymal interactions, increasing
in the BALFs of IPF patients and they were associated
with fibroblast recruitment and vascular leakage. fibroblast proliferation and excessive synthesis of collagen
43
47
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is a bioactive eicosanoid that and ECM. The origin and activation of fibroblasts and
regulates many important biological processes. PGE2 myofibroblasts in IPF remain controversial. Studies have
signaling has multiple inhibitory effects on lung cells, shown that AECs can transform into myofibroblasts via
including limiting fibroblast proliferation, migration, EMT under the action of TGF-β, with the ECM being a
48
and collagen production, all of which potentially key regulator. EMT contributes to the fibrotic cascade
suppress fibrosis. IPF patients often show a reduced in IPF by altering AEC characteristics – morphology,
production of prostaglandins. Transforming growth adhesion, migration, and resistance to apoptosis – while
44
factor (TGF)-β, a highly conserved cytokine family, increasing matrix metalloproteinase expression and ECM
has a significant impact on fibroblasts, contributing to degradation. 49
the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis (Figure 2). 28 11. miRNA in the diagnosis of IPF
TGF-β facilitates epithelial cell migration, synthesis of
collagen, proliferation of fibroblast, and myofibroblast miRNAs are crucial players not only in the biological
transdifferentiation. 45 development and cell differentiation processes but also
Volume 11 Issue 2 (2025) 34 doi: 10.36922/JCTR025080009