Page 38 - JCTR-11-2
P. 38
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research miRNA in pneumonia and pulmonary fibrosis
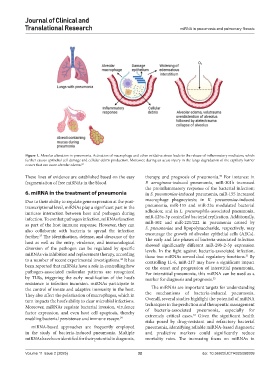
Figure 1. Alveolar alteration in pneumonia. Activation of macrophage and other oxidative stress leads to the release of inflammatory mediators, which
further causes epithelial cell damage and cellular debris production. Moreover, during an acute injury in the lungs degradation of the capillary barrier
occurs that can cause alveolar edema. 69
These lines of evidence are established based on the easy therapy, and prognosis of pneumonia. For instance: in
30
fragmentation of free miRNAs in the blood. P. aeruginosa-induced pneumonia, miR-301b increased
the proinflammatory response of the bacterial infection;
6. miRNA in the treatment of pneumonia in S. pneumoniae-induced pneumonia, miR-155 increased
Due to their ability to regulate gene expression at the post- macrophage phagocytosis; in K. pneumoniae-induced
transcriptional level, miRNAs play a significant part in the pneumonia, miR-155 and miR-23a modulated bacterial
intricate interaction between host and pathogen during adhesion; and in L. pneumophila-associated pneumonia,
infection. To combat pathogen infection, miRNAs function miR-125a-3p controlled bacterial replication. Additionally,
as part of the host immune response. However, they can miR-302 and miR-221/222 in pneumonia caused by
also collaborate with bacteria to spread the infection S. pneumoniae and lipopolysaccharide, respectively, may
encourage the growth of alveolar epithelial cells (AECs).
further. The identification, defense, and clearance of the The early and late phases of bacteria-associated infection
27
host as well as the entry, virulence, and immunological showed significantly different miR-29b-2-5p expression
diversion of the pathogen can be regulated by specific levels. In the fight against bacteria-associated infection,
miRNAs via inhibition and replacement therapy, according these two miRNAs served dual regulatory functions. By
31
to a number of recent experimental investigations. It has controlling IL-6, miR-217 may have a significant impact
28
been reported that miRNAs have a role in controlling how on the onset and progression of interstitial pneumonia.
pathogen-associated molecular patterns are recognized For interstitial pneumonia, this miRNA can be used as a
by TLRs, triggering the early modification of the host’s marker for diagnosis and prognosis. 32
resistance to infection incursion. miRNAs participate in
the control of innate and adaptive immunity in the host. The miRNAs are important targets for understanding
They also affect the polarization of macrophages, which in the mechanisms of bacteria-induced pneumonia.
turn impacts the host’s ability to clear microbial infections. Overall, several studies highlight the potential of miRNA
Moreover, miRNAs regulate bacterial invasion, virulence techniques in the prediction and therapeutic management
of bacteria-associated pneumonia, especially for
factor expression, and even host cell apoptosis, thereby extremely critical cases. Given the significant health
33
enabling bacterial persistence and immune escape. 29
risks posed by drug-resistant and refractory bacterial
miRNA-based approaches are frequently employed pneumonia, identifying reliable miRNA-based diagnostic
in the study of bacteria-induced pneumonia. Multiple and predictive markers could significantly reduce
miRNAs have been identified for their potential in diagnosis, mortality rates. The increasing focus on miRNAs in
Volume 11 Issue 2 (2025) 32 doi: 10.36922/JCTR025080009